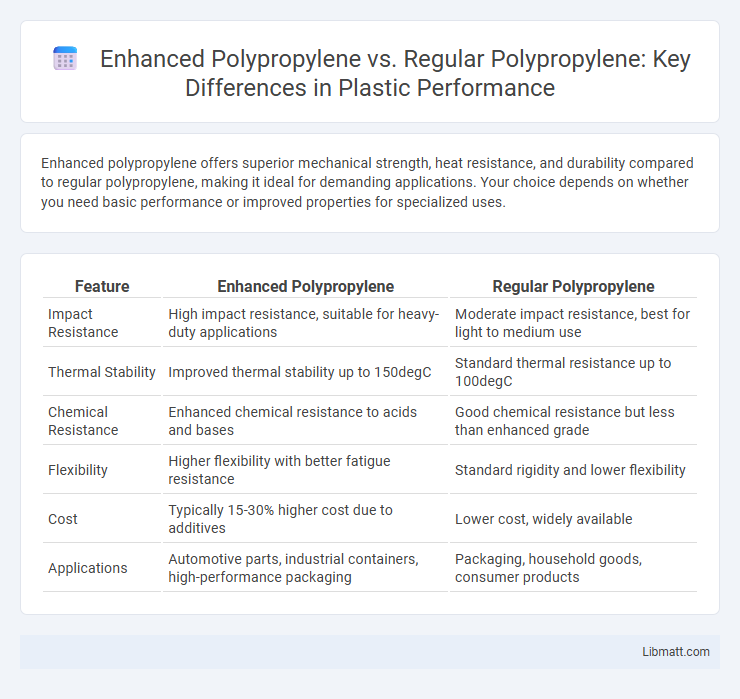
Enhanced polypropylene offers superior mechanical strength, heat resistance, and durability compared to regular polypropylene, making it ideal for demanding applications. Your choice depends on whether you need basic performance or improved properties for specialized uses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Enhanced Polypropylene | Regular Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance, suitable for heavy-duty applications | Moderate impact resistance, best for light to medium use |
| Thermal Stability | Improved thermal stability up to 150degC | Standard thermal resistance up to 100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Enhanced chemical resistance to acids and bases | Good chemical resistance but less than enhanced grade |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility with better fatigue resistance | Standard rigidity and lower flexibility |
| Cost | Typically 15-30% higher cost due to additives | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Automotive parts, industrial containers, high-performance packaging | Packaging, household goods, consumer products |
Introduction to Polypropylene: Types and Applications
Enhanced polypropylene exhibits superior mechanical properties, including increased impact resistance and thermal stability, compared to regular polypropylene. Regular polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer, is widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to its lightweight and chemical resistance. Applications of enhanced polypropylene extend to more demanding sectors such as aerospace, medical devices, and advanced automotive components where improved durability and performance are critical.
What is Regular Polypropylene?
Regular polypropylene is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its balance of strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance. It is commonly utilized in packaging, automotive parts, and textiles due to its lightweight and durability. Your choice of polypropylene affects the performance of products in terms of heat resistance and impact strength.
Defining Enhanced Polypropylene
Enhanced polypropylene is a modified form of regular polypropylene that incorporates additives or fillers to improve mechanical properties such as impact resistance, tensile strength, and thermal stability. Unlike standard polypropylene, enhanced variants are engineered to withstand harsher conditions and offer superior durability for automotive, packaging, and construction applications. The optimized polymer matrix in enhanced polypropylene delivers better performance in demanding environments while maintaining lightweight characteristics.
Key Differences Between Enhanced and Regular Polypropylene
Enhanced polypropylene offers superior mechanical strength, higher impact resistance, and improved thermal stability compared to regular polypropylene. Your applications benefit from enhanced polypropylene's better chemical resistance and longer lifespan under harsh conditions. These key differences make enhanced polypropylene ideal for more demanding industrial and automotive uses where durability and performance are critical.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Enhanced Polypropylene exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to Regular Polypropylene, including increased tensile strength, improved impact resistance, and greater flexural modulus. These enhancements result from the incorporation of additives or fillers that improve durability and stiffness, making Enhanced Polypropylene ideal for demanding applications. Your choice of material impacts product performance, especially in automotive components or packaging requiring higher mechanical resilience.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Enhanced polypropylene offers superior chemical resistance compared to regular polypropylene, making it more suitable for applications involving exposure to harsh chemicals or solvents. Its improved molecular structure increases durability, providing greater resistance to wear, impact, and environmental stress. Choosing enhanced polypropylene ensures your products maintain integrity and longevity in demanding conditions.
Processing and Manufacturing Variations
Enhanced polypropylene offers superior processing advantages over regular polypropylene, including improved melt strength and flow properties that facilitate complex molding techniques. Your manufacturing process benefits from faster cycle times and reduced warping due to enhanced thermal stability and dimensional consistency. These variations result in higher-quality finished products with better mechanical performance compared to those produced with standard polypropylene.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Enhanced polypropylene features improved recyclability due to additives that facilitate easier sorting and processing, reducing environmental waste compared to regular polypropylene. Its formulation often includes bio-based or recycled content, significantly lowering carbon footprint and reliance on virgin fossil fuels. Regular polypropylene, while widely recyclable, typically results in higher landfill volumes and less efficient recycling streams due to contamination and material degradation.
Cost Implications and Market Availability
Enhanced polypropylene offers superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance compared to regular polypropylene, resulting in higher production costs that impact overall pricing. Market availability of enhanced polypropylene is more limited due to specialized manufacturing processes and niche applications, while regular polypropylene is widely produced and readily accessible across various industries. Cost implications involve balancing performance benefits with budget constraints, influencing material selection based on project requirements and supply chain considerations.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene for Your Application
Enhanced polypropylene offers superior impact resistance, heat tolerance, and chemical stability compared to regular polypropylene, making it ideal for demanding industrial and automotive applications. Regular polypropylene remains a cost-effective option for everyday packaging, consumer goods, and low-stress components. You should evaluate your application's specific requirements, including durability and environmental factors, to select the most suitable polypropylene type.
Enhanced Polypropylene vs Regular Polypropylene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com