ISO molding standards focus on international consistency and compatibility, ensuring product uniformity across global markets, while DIN molding adheres to German-specific regulations emphasizing precision and durability for industrial applications. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize worldwide standardization or region-specific technical requirements in molding processes.
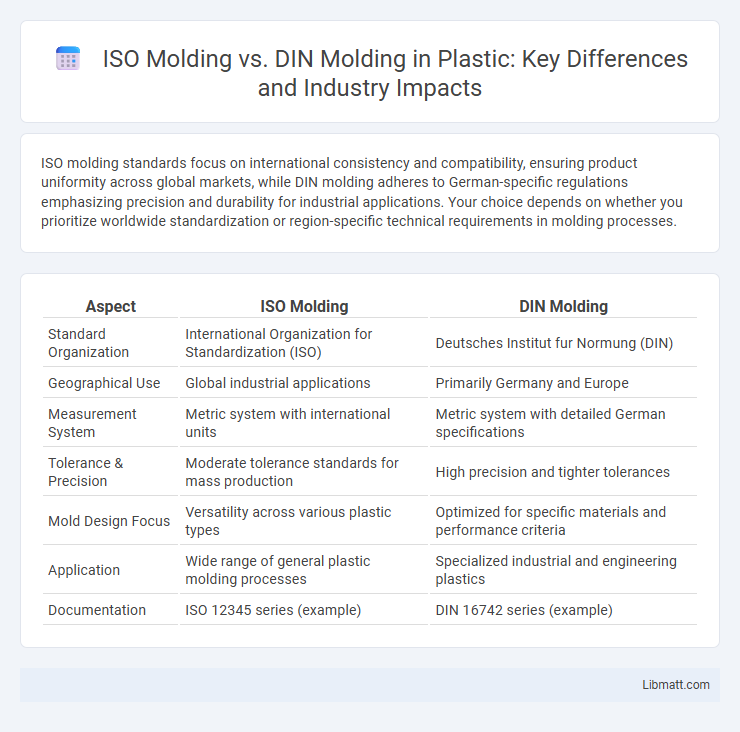
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | ISO Molding | DIN Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Organization | International Organization for Standardization (ISO) | Deutsches Institut fur Normung (DIN) |
| Geographical Use | Global industrial applications | Primarily Germany and Europe |
| Measurement System | Metric system with international units | Metric system with detailed German specifications |
| Tolerance & Precision | Moderate tolerance standards for mass production | High precision and tighter tolerances |
| Mold Design Focus | Versatility across various plastic types | Optimized for specific materials and performance criteria |
| Application | Wide range of general plastic molding processes | Specialized industrial and engineering plastics |
| Documentation | ISO 12345 series (example) | DIN 16742 series (example) |
Introduction to ISO and DIN Molding Standards
ISO molding standards, established by the International Organization for Standardization, provide globally recognized guidelines ensuring consistent quality and compatibility in molded parts across various industries. DIN molding standards, developed by the Deutsches Institut fur Normung, emphasize precision and technical specifications primarily used in German engineering and manufacturing sectors. Both standards facilitate reliable production processes but differ in regional adoption and specific technical requirements for molding applications.
Overview of ISO Molding
ISO molding follows international standards set by the International Organization for Standardization, ensuring consistent quality and compatibility across global markets. It emphasizes precision in dimensions, material properties, and molding processes to meet stringent quality control requirements. Manufacturers adopting ISO molding benefit from enhanced product reliability and streamlined supply chain integration worldwide.
Overview of DIN Molding
DIN molding refers to the standardized moldings defined by the Deutsches Institut fur Normung (DIN), which specifies precise dimensions and tolerances to ensure compatibility and interchangeability across various engineering and manufacturing sectors. This molding system is widely used in Europe and emphasizes strict adherence to quality, durability, and performance standards, making it suitable for industrial applications requiring high precision. DIN molding components are designed to integrate seamlessly with standardized parts, facilitating streamlined production processes and reducing manufacturing complexities.
Key Differences Between ISO and DIN Molding
ISO molding standards emphasize global compatibility and dimensional accuracy, facilitating international trade and uniform production processes. DIN molding, rooted in German industrial specifications, prioritizes precision and material quality tailored for European markets. Key differences lie in their tolerance ranges, measurement systems, and regional application focus, with ISO being more universally applicable and DIN offering stricter engineering criteria.
Material Compatibility in ISO vs DIN Molding
ISO molding standards provide broader material compatibility, supporting a wider range of polymers and composites due to their global adoption and versatile specifications. DIN molding primarily focuses on standardized materials common in European industries, emphasizing plastics like PVC, PE, and PA, which ensures strict conformity but limits diverse material options. Both standards ensure high-quality molding processes, but ISO's material compatibility facilitates greater flexibility in selecting raw materials for varied industrial applications.
Dimensional Tolerances: ISO vs DIN
ISO molding standards specify dimensional tolerances with a broader range, allowing for more flexibility in manufacturing processes, which can be beneficial for large-scale production with varied applications. DIN molding standards impose stricter dimensional tolerances, ensuring higher precision and consistency, ideal for components requiring exact fits and tight quality control. Your choice between ISO and DIN molding should consider the balance between required precision and production cost efficiency.
Application Areas for ISO and DIN Molding
ISO molding standards are widely applied in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics industries due to their strict quality control and international recognition. DIN molding is commonly used in European markets, particularly in industrial machinery and electrical equipment manufacturing, where precise dimensional tolerances and compatibility with German engineering standards are critical. Your choice between ISO and DIN molding should consider the specific application requirements and regional industry standards to ensure optimal performance and compliance.
Quality Control: ISO Molding vs DIN Molding
ISO molding adheres to internationally recognized standards that emphasize rigorous quality control processes, ensuring consistent product reliability and global compatibility. In contrast, DIN molding follows German industrial standards known for precise manufacturing tolerances and strict quality assurance metrics tailored to regional requirements. Your choice between ISO and DIN molding should consider the specific quality control protocols that align with your project's compliance needs and performance expectations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Standard
ISO molding offers standardized global compatibility and consistent quality control, enhancing international trade and manufacturing efficiency, but may involve higher certification costs and stricter compliance requirements. DIN molding provides robust precision engineering tailored to European industrial norms, facilitating local supplier accessibility and cost-effective production, although it can limit interoperability outside the DIN-centric regions. Both standards impact tooling design, material selection, and dimensional tolerances, influencing product performance and market acceptance depending on regional industry demands.
Choosing the Right Standard: ISO or DIN Molding
Choosing the right molding standard between ISO and DIN depends on the specific industry requirements and geographic market demands. ISO molding standards offer global compatibility and are widely accepted across international markets, ensuring consistency in quality and dimensions. DIN molding standards, predominantly used in Germany and surrounding regions, are preferred for precision engineering applications due to their stringent technical specifications.
ISO Molding vs DIN Molding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com