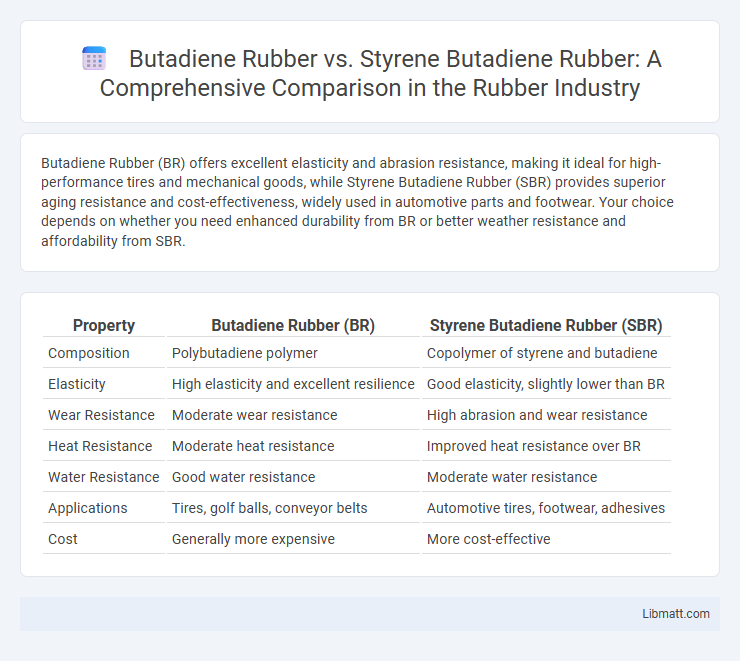
Butadiene Rubber (BR) offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance tires and mechanical goods, while Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) provides superior aging resistance and cost-effectiveness, widely used in automotive parts and footwear. Your choice depends on whether you need enhanced durability from BR or better weather resistance and affordability from SBR.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butadiene Rubber (BR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polybutadiene polymer | Copolymer of styrene and butadiene |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and excellent resilience | Good elasticity, slightly lower than BR |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | High abrasion and wear resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | Improved heat resistance over BR |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Applications | Tires, golf balls, conveyor belts | Automotive tires, footwear, adhesives |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More cost-effective |
Introduction to Butadiene Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Butadiene Rubber (BR) is a synthetic rubber produced from the polymerization of 1,3-butadiene, known for its excellent wear resistance and high resilience, making it ideal for tire manufacturing and industrial applications. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, combining the strength and abrasion resistance of styrene with the flexibility and low-temperature performance of butadiene, widely used in automotive tires, footwear, and adhesives. Both polymers are critical in the rubber industry, with SBR offering enhanced processability and cost-effectiveness compared to BR.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Butadiene rubber (BR) consists of repeating units derived from 1,3-butadiene, forming a polymer chain with high cis-1,4 content, which imparts excellent elasticity and low glass transition temperature. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, where styrene units introduce increased polarity and rigidity due to the phenyl group, resulting in enhanced abrasion resistance and processability. The chemical structure difference, with BR's pure conjugated diene backbone versus SBR's alternating styrene and butadiene monomers, governs their distinct mechanical and thermal properties essential for applications like tires and industrial products.
Production Processes
Butadiene Rubber (BR) is produced primarily through emulsifier polymerization of 1,3-butadiene monomers, resulting in a high-purity polymer with excellent wear resistance and tensile strength. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is synthesized via emulsion or solution polymerization by copolymerizing styrene and butadiene, offering greater versatility with improved abrasion resistance and aging properties. Your choice between BR and SBR depends on the desired balance of elasticity, durability, and production method efficiency.
Key Physical Properties
Butadiene Rubber (BR) is known for its high resilience, excellent wear resistance, and low glass transition temperature, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility at low temperatures. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers improved abrasion resistance, good aging stability, and better heat resistance compared to BR, due to its styrene content. Your choice between BR and SBR should consider factors like tensile strength, hardness, and temperature performance based on the specific demands of your application.
Mechanical Performance
Butadiene Rubber (BR) exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and high elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers superior tensile strength and aging resistance due to its styrene content, enhancing mechanical stability in harsh environments. While BR excels in low-temperature performance, SBR provides better overall wear resistance and is widely used in tire manufacturing for its balanced mechanical properties.
Applications and Uses
Butadiene Rubber (BR) excels in manufacturing tires, conveyor belts, and mechanical goods due to its high abrasion resistance, while Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is widely used in automotive tires, footwear, and adhesives for its superior aging stability and balanced wear resistance. SBR offers better resistance to heat and oxidation, making it ideal for synthetic rubber applications in tires and industrial products, whereas BR's low rolling resistance and flexibility suit it for high-performance tire treads and industrial parts. Both rubbers are essential in the tire industry, with SBR dominating passenger vehicle tires and BR favored in racing tires and heavy-duty applications.
Advantages of Butadiene Rubber
Butadiene Rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and excellent low-temperature flexibility compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber, making it ideal for high-performance tire applications and industrial uses. Its high resilience and good wear resistance enhance durability in demanding environments, ensuring longer service life. If you require materials that withstand harsh mechanical stress and extreme temperatures, Butadiene Rubber provides significant advantages over Styrene Butadiene Rubber.
Benefits of Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and aging stability compared to Butadiene Rubber (BR), making it ideal for high-performance tire treads and industrial applications. Its superior grip and durability improve safety and longevity in automotive components, while resistance to heat and oxidation ensures consistent performance under demanding conditions. Choosing SBR can optimize your product's overall resilience and lifespan, especially in environments requiring robust mechanical properties.
Cost and Availability
Butadiene Rubber (BR) generally offers lower production costs compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) due to its simpler polymerization process and higher availability of raw materials. SBR tends to be more expensive because it incorporates styrene, which increases the complexity and cost of synthesis while also offering improved abrasion resistance and aging properties. In terms of availability, BR is primarily sourced from butadiene monomers derived from petroleum refining, whereas SBR benefits from a wider market presence due to its extensive use in tire manufacturing and other rubber goods.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Butadiene Rubber (BR) and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) differ in their environmental impact and safety profiles due to variations in chemical composition and production processes. SBR typically involves higher styrene content, which can pose greater risks of volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and associated air quality concerns during manufacturing, whereas BR production generally generates fewer hazardous emissions. When selecting materials for your projects, consider SBR's potential environmental regulatory compliance challenges and BR's comparatively lower toxicity for safer handling and reduced ecological footprint.
Butadiene Rubber vs Styrene Butadiene Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com