Closed mixing prevents environmental noise interference by using an isolated environment or software setup, ensuring precise control over sound elements. Open mixing allows ambient sounds and real-time collaboration, offering a more organic and spontaneous creative process that can enhance your music's natural feel.
Table of Comparison
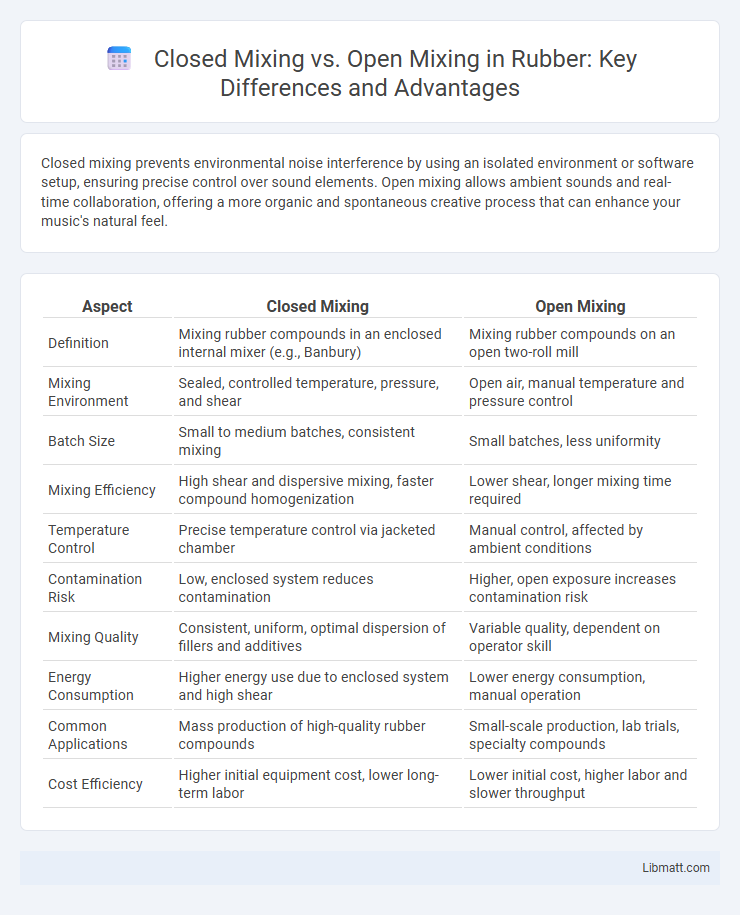
| Aspect | Closed Mixing | Open Mixing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mixing rubber compounds in an enclosed internal mixer (e.g., Banbury) | Mixing rubber compounds on an open two-roll mill |
| Mixing Environment | Sealed, controlled temperature, pressure, and shear | Open air, manual temperature and pressure control |
| Batch Size | Small to medium batches, consistent mixing | Small batches, less uniformity |
| Mixing Efficiency | High shear and dispersive mixing, faster compound homogenization | Lower shear, longer mixing time required |
| Temperature Control | Precise temperature control via jacketed chamber | Manual control, affected by ambient conditions |
| Contamination Risk | Low, enclosed system reduces contamination | Higher, open exposure increases contamination risk |
| Mixing Quality | Consistent, uniform, optimal dispersion of fillers and additives | Variable quality, dependent on operator skill |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use due to enclosed system and high shear | Lower energy consumption, manual operation |
| Common Applications | Mass production of high-quality rubber compounds | Small-scale production, lab trials, specialty compounds |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial equipment cost, lower long-term labor | Lower initial cost, higher labor and slower throughput |
Introduction to Closed and Open Mixing
Closed mixing involves processing materials within sealed systems to prevent contamination and control environmental factors, commonly used in pharmaceutical and food industries for enhanced safety and product consistency. Open mixing allows exposure to the atmosphere, making it suitable for materials that require ventilation or moisture evaporation during blending, often utilized in construction and chemical processing. Selecting between closed and open mixing depends on product sensitivity, contamination risk, and processing requirements.
Defining Closed Mixing
Closed mixing involves blending ingredients within a sealed environment to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity, often used in pharmaceuticals and food processing. This method enhances safety by minimizing exposure to air, moisture, and external particles, ensuring consistent quality in Your final mixture. Equipment typically includes airtight mixers and reactors designed for controlled pressure and temperature conditions.
Understanding Open Mixing
Open mixing involves blending ingredients in an exposed environment, allowing for easier monitoring and adjustments during the process. Its advantages include better heat dissipation and ease of access for quality checks, making it ideal for small-scale or experimental batches. Understanding open mixing can help you optimize your formulation when flexibility and visibility are essential.
Key Differences Between Closed and Open Mixing
Closed mixing involves combining ingredients in a sealed environment to prevent contamination and control exposure to air, moisture, and dust, ensuring product consistency and safety. Open mixing occurs in an exposed environment, allowing for easier monitoring and adjustment but increasing the risk of contamination and loss of volatile components. Your choice between closed and open mixing depends on product sensitivity, operational control, and cleanliness requirements.
Benefits of Closed Mixing Techniques
Closed mixing techniques minimize contamination risks by operating within sealed environments, ensuring higher product purity and consistency especially in pharmaceuticals and food industries. These methods reduce exposure to external air and moisture, leading to improved material stability and shelf life. Enhanced safety for operators is achieved by containing dust and fumes, making closed mixing a preferred choice for hazardous or sensitive materials.
Advantages of Open Mixing Approaches
Open mixing approaches offer enhanced flexibility for real-time adjustments and easier integration with continuous production lines, boosting overall efficiency. These methods allow superior scalability and improved temperature control, resulting in more consistent product quality. Furthermore, open mixing facilitates thorough cleaning and maintenance, reducing downtime and contamination risks.
Common Challenges in Both Mixing Methods
Both closed mixing and open mixing face common challenges such as maintaining uniform ingredient distribution and preventing contamination during the process. Ensuring consistent mixing time and speed is critical in both methods to achieve product homogeneity and quality. Your ability to monitor and control these variables directly affects the efficiency and outcome of the mixing operation.
Applications in Industry and Music Production
Closed mixing environments provide precise control over sound reflections, making them ideal for high-end music production studios and broadcast facilities where audio accuracy is paramount. Open mixing setups are commonly used in live sound reinforcement and industrial settings that require flexibility and natural acoustics, such as concert venues and large-scale manufacturing plants. Your choice between closed and open mixing depends on whether you prioritize controlled sound engineering or adaptable, ambient sound capture for the application.
Choosing the Right Mixing Method for Your Project
Closed mixing provides a controlled environment that minimizes contamination and volatile loss, ideal for sensitive materials or reactive chemicals requiring precise handling. Open mixing offers easier access and flexibility, better suited for large batch sizes or processes where thorough aeration and temperature control are less critical. Selecting the right method depends on project specifications such as material sensitivity, batch volume, and environmental control requirements to ensure optimal mixing efficiency and product consistency.
Future Trends in Mixing Technologies
Future trends in mixing technologies emphasize enhanced automation and precise control within closed mixing systems to ensure contamination-free environments for pharmaceuticals and food processing. Open mixing systems are evolving with improved energy efficiency and adaptive mixing blades, optimizing industrial batch sizes and reducing operational costs. Integration of AI-driven sensors and real-time data analytics is shaping both closed and open mixers to achieve superior process consistency and product quality.
Closed Mixing vs Open Mixing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com