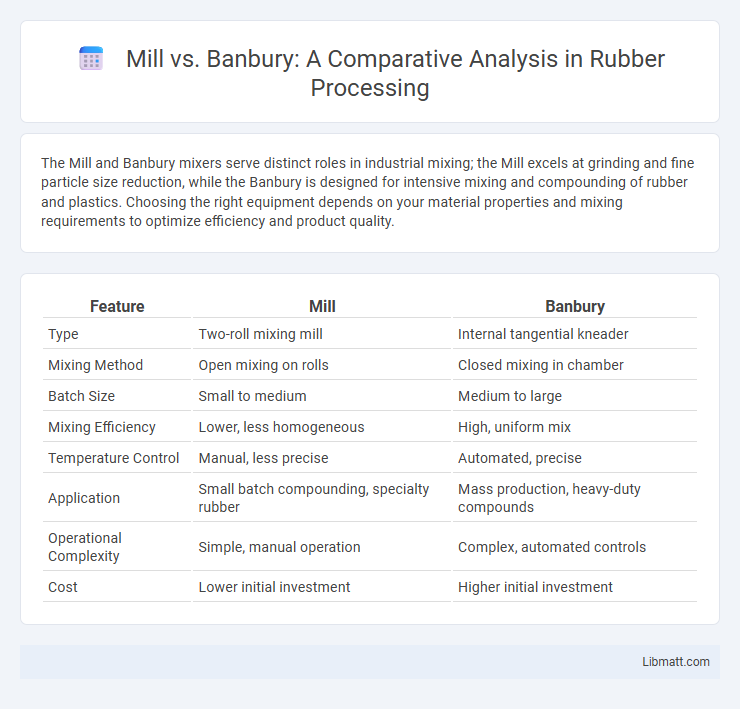
The Mill and Banbury mixers serve distinct roles in industrial mixing; the Mill excels at grinding and fine particle size reduction, while the Banbury is designed for intensive mixing and compounding of rubber and plastics. Choosing the right equipment depends on your material properties and mixing requirements to optimize efficiency and product quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mill | Banbury |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Two-roll mixing mill | Internal tangential kneader |
| Mixing Method | Open mixing on rolls | Closed mixing in chamber |
| Batch Size | Small to medium | Medium to large |
| Mixing Efficiency | Lower, less homogeneous | High, uniform mix |
| Temperature Control | Manual, less precise | Automated, precise |
| Application | Small batch compounding, specialty rubber | Mass production, heavy-duty compounds |
| Operational Complexity | Simple, manual operation | Complex, automated controls |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Mill and Banbury Mixing Machines
Mill and Banbury mixing machines are essential in the rubber and plastics industries for blending raw materials efficiently. The Banbury mixer utilizes a powerful, enclosed system with intermeshing rotors to create homogeneous compounds rapidly, while the mill consists of two counter-rotating rolls primarily used for shearing and refining materials. Your choice between these machines depends on factors such as production scale, material type, and mixing precision requirements.
Historical Development of Mill and Banbury Technology
The historical development of Mill and Banbury technology traces back to the early 19th century when the traditional roller mill was adapted for rubber and polymer mixing, evolving into the modern two-roll mill system. The Banbury mixer, invented in 1916 by Fernley H. Banbury, introduced a powerful internal mixer design that significantly improved the efficiency and uniformity of mixing rubber compounds. Advances in material science and engineering throughout the 20th century have refined both technologies, resulting in optimized mixing processes crucial for the production of high-performance elastomers and composites.
Key Components of Mill Mixers
Mill mixers, including Banbury and traditional mills, rely on key components such as the mixing chamber, rotors, and cooling system to efficiently blend rubber compounds. The Banbury mixer features intermeshing rotors within a closed mixing chamber, providing high shear and effective dispersion of ingredients. Precise temperature control via a robust cooling system ensures optimal reaction conditions and consistent compound quality.
Structure and Function of Banbury Mixers
Banbury mixers feature a robust, enclosed robust steel construction designed to withstand high pressure and shear forces during mixing, ensuring durability and efficient operation. The internal mixing chamber contains two intermeshing rotors rotating at different speeds to create intense mechanical shear and dispersive mixing, ideal for blending rubber and plastic compounds. This precise rotor design optimizes heat generation and material flow, allowing you to achieve uniform compound consistency and enhanced mixing quality.
Comparing Mixing Mechanisms: Mill vs Banbury
The Mill uses shear and compression between two rotating rollers to mix materials, ideal for rubber and plastics requiring thorough blending. The Banbury mixer employs an internal rotor system that combines high-intensity mixing with efficient heat dissipation, making it suitable for large batches and complex formulations. Your choice depends on the material viscosity and batch size, with Mills offering precise control and Banburys providing faster, high-volume mixing.
Processing Efficiency: Advantages and Limitations
Mill processing offers high efficiency in large-scale production by enabling continuous operation and uniform particle size reduction, optimizing throughput in industries such as cement and mining. Banbury mixers excel in blending efficiency, ensuring thorough mixing of polymers and additives through intense shear forces, ideal for rubber and plastic compounding. However, mills may face limitations in handling heat-sensitive materials due to frictional heat buildup, while Banbury mixers require careful temperature control to prevent degradation during high-intensity mixing.
Material Compatibility for Mill and Banbury
Mill and Banbury mixers both handle different materials effectively, but their compatibility depends on material properties like viscosity and particle size. Mills are ideal for less viscous substances such as rubber and plastic compounds, while Banbury mixers excel with highly viscous materials and complex blends, offering thorough mixing and dispersion. Understanding your material's rheology ensures optimal equipment selection for efficient processing and consistent product quality.
Energy Consumption and Operational Costs
Mill systems generally exhibit higher energy consumption compared to Banbury mixers due to their longer processing times and less efficient heat management. Banbury mixers optimize operational costs by providing faster mixing cycles and better energy utilization, resulting in reduced electricity expenses for industrial users. Choosing the Banbury mixer can enhance your production efficiency while lowering overall energy and operational costs.
Safety and Maintenance Considerations
Mill and Banbury mixers exhibit distinct safety and maintenance profiles crucial for industrial applications. Banbury mixers require rigorous safety protocols due to high-torque operation and enclosed mixing chambers, necessitating regular inspection of seals and blades to prevent mechanical failure and contamination. Mill systems demand consistent maintenance of rollers and cooling components to ensure material integrity and operator safety, with emphasis on lubrication and alignment checks to avert equipment wear and overheating.
Industrial Applications and Future Trends
Mill and Banbury mixers serve critical roles in industrial applications, with mills primarily used for refining and blending rubber or plastic compounds, while Banbury mixers excel in heavy-duty mixing of viscous materials like rubber, plastics, and additives. Advances in automation and real-time monitoring systems are optimizing the efficiency and precision of both mixers, enabling higher throughput and consistent product quality. Your manufacturing process can benefit from integrating these future trends, ensuring adaptability to evolving material science and production demands.
Mill vs Banbury Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com