Hot air vulcanization uses heated air to cure rubber, providing uniform temperature control and reduced moisture-related defects, ideal for sensitive rubber compounds. Steam vulcanization relies on pressurized steam to transfer heat quickly, offering faster processing times and efficient energy use, making it suitable for large-scale rubber manufacturing.
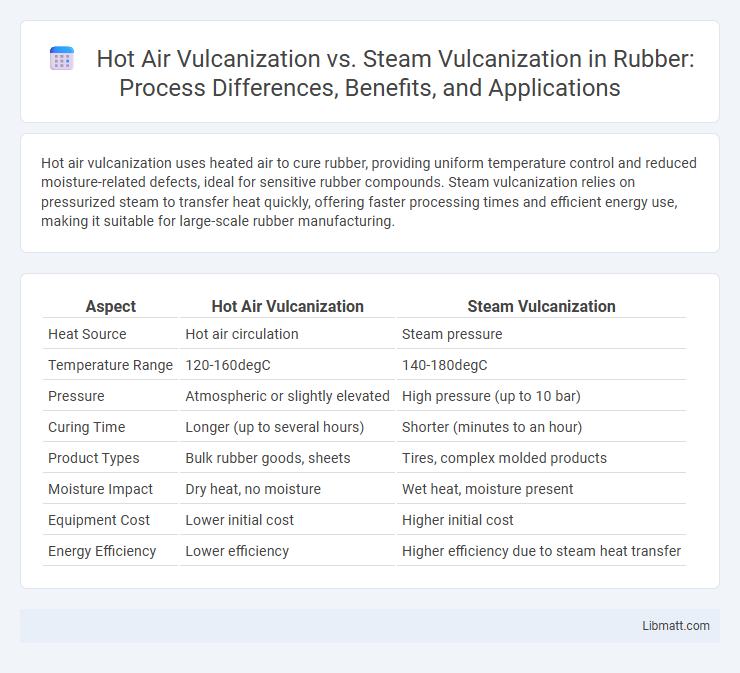
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hot Air Vulcanization | Steam Vulcanization |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Hot air circulation | Steam pressure |
| Temperature Range | 120-160degC | 140-180degC |
| Pressure | Atmospheric or slightly elevated | High pressure (up to 10 bar) |
| Curing Time | Longer (up to several hours) | Shorter (minutes to an hour) |
| Product Types | Bulk rubber goods, sheets | Tires, complex molded products |
| Moisture Impact | Dry heat, no moisture | Wet heat, moisture present |
| Equipment Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower efficiency | Higher efficiency due to steam heat transfer |
Introduction to Vulcanization Processes
Hot air vulcanization uses heated air to cure rubber, providing even heat distribution and precise temperature control ideal for delicate compounds. Steam vulcanization relies on saturated steam to transfer heat rapidly, accelerating the curing process and enhancing production efficiency in large-scale applications. Both methods optimize rubber's mechanical properties by cross-linking polymer chains, but differ significantly in heat delivery and suitability based on material sensitivity and manufacturing speed requirements.
Understanding Hot Air Vulcanization
Hot air vulcanization uses heated air to cure rubber compounds, offering precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution for consistent cross-linking. This method reduces moisture exposure, making it ideal for materials sensitive to steam or water. Hot air vulcanization ensures improved product quality and durability in applications requiring clean processing environments.
Steam Vulcanization Overview
Steam vulcanization uses pressurized steam to accelerate the curing process of rubber, enhancing its elasticity and strength through cross-linking of polymer chains. This method provides uniform heat distribution, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications such as tire manufacturing. Steam vulcanization typically operates at temperatures between 140degC and 160degC with controlled pressure to ensure consistent product quality and improved mechanical properties.
Key Differences: Hot Air vs Steam Vulcanization
Hot air vulcanization uses heated air at temperatures typically between 150degC and 200degC, providing uniform heat transfer for curing rubber products, while steam vulcanization employs saturated steam at around 120degC to 160degC, offering faster heat penetration due to steam's higher thermal conductivity. Hot air vulcanization is preferred for drying and curing thin or delicate rubber items, whereas steam vulcanization suits bulkier products requiring rapid and consistent heat exposure. The selection between hot air and steam vulcanization depends on factors like material thickness, production speed, and energy efficiency.
Process Efficiency Comparison
Hot air vulcanization offers faster heating cycles and more precise temperature control compared to steam vulcanization, resulting in improved process efficiency for certain rubber compounds. Steam vulcanization provides better heat penetration and uniformity, especially for thicker products, but typically requires longer cycle times due to slower temperature ramp-up and cooldown phases. Your choice between hot air and steam vulcanization should consider the specific material properties and production speed requirements to optimize throughput and energy consumption.
Impact on Rubber Properties
Hot air vulcanization produces rubber with enhanced surface hardness and better resistance to oxidation due to the dry heat environment, improving durability in harsh conditions. Steam vulcanization, by providing uniform heat and moisture, results in rubber with superior elasticity and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility. The choice between hot air and steam vulcanization directly influences the mechanical properties and service life of the vulcanized rubber products.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Concerns
Hot air vulcanization generally consumes more energy due to longer heating times and higher temperature requirements compared to steam vulcanization, which uses saturated steam to transfer heat more efficiently. Steam vulcanization produces less environmental impact since it relies on water vapor, reducing emissions of greenhouse gases associated with fossil fuel combustion. You can reduce your carbon footprint by choosing steam vulcanization for its lower energy consumption and cleaner process.
Cost Implications of Both Methods
Hot air vulcanization generally incurs higher operational costs due to longer curing times and increased energy consumption compared to steam vulcanization, which benefits from faster heat transfer and reduced cycle durations. Steam vulcanization offers cost efficiency through lower fuel usage and improved throughput, making it more suitable for large-scale production runs. Equipment maintenance expenses tend to be higher with hot air systems due to temperature control complexities and wear from prolonged high-temperature exposure.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Hot air vulcanization is widely used in industries requiring precise temperature control and uniform heating, such as aerospace and electronics, where delicate components need consistent curing without moisture exposure. Steam vulcanization suits heavy-duty rubber products in automotive, construction, and industrial hose manufacturing due to its efficient heat transfer and ability to penetrate thick rubber layers. Your choice depends on the material thickness and sensitivity, with hot air ideal for thin or heat-sensitive items and steam preferred for bulkier, moisture-tolerant applications.
Choosing the Right Vulcanization Technique
Choosing the right vulcanization technique depends on the specific material properties and production requirements. Hot air vulcanization offers precise temperature control ideal for delicate rubber compounds, while steam vulcanization provides faster curing times and uniform heat distribution suited for large-scale manufacturing. Evaluating factors such as curing time, energy efficiency, and rubber thickness is essential to optimize product quality and manufacturing costs.
Hot air vulcanization vs Steam vulcanization Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com