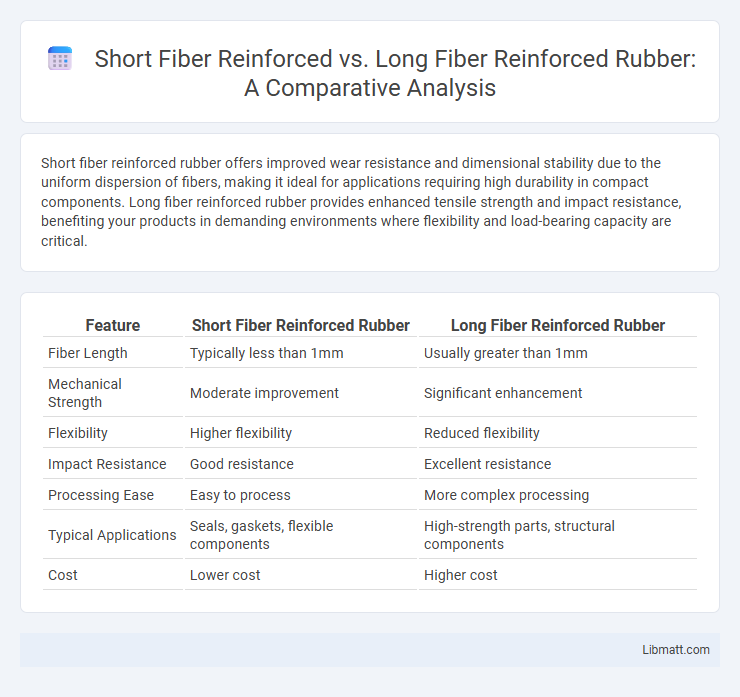
Short fiber reinforced rubber offers improved wear resistance and dimensional stability due to the uniform dispersion of fibers, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability in compact components. Long fiber reinforced rubber provides enhanced tensile strength and impact resistance, benefiting your products in demanding environments where flexibility and load-bearing capacity are critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Short Fiber Reinforced Rubber | Long Fiber Reinforced Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | Typically less than 1mm | Usually greater than 1mm |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate improvement | Significant enhancement |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility | Reduced flexibility |
| Impact Resistance | Good resistance | Excellent resistance |
| Processing Ease | Easy to process | More complex processing |
| Typical Applications | Seals, gaskets, flexible components | High-strength parts, structural components |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforced Rubber Composites
Fiber reinforced rubber composites enhance mechanical properties by embedding fibers into the rubber matrix, improving strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Short fiber reinforced rubber offers better isotropic properties and easier processing due to uniform fiber distribution, while long fiber reinforced rubber provides superior tensile strength and load transfer capabilities because of continuous fiber alignment. Your choice between short and long fiber reinforcement depends on the specific performance requirements and manufacturing constraints of the application.
Overview of Short Fiber Reinforced Rubber
Short fiber reinforced rubber integrates fine, chopped fibers to enhance mechanical properties such as tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and dimensional stability. The fiber lengths typically range from 0.1 to 1 mm, enabling improved load transfer within the rubber matrix without significantly compromising flexibility. This reinforcement method is widely used in automotive and industrial applications where balanced performance and processability are critical.
Overview of Long Fiber Reinforced Rubber
Long fiber reinforced rubber incorporates continuous or semi-continuous fibers that significantly enhance mechanical properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and dimensional stability compared to short fiber reinforced composites. The long fibers create a more effective load transfer network within the rubber matrix, resulting in improved durability and performance under dynamic conditions. Your applications requiring high wear resistance and structural integrity benefit greatly from long fiber reinforced rubber's superior reinforcement characteristics.
Differences in Microstructural Characteristics
Short fiber reinforced rubber features randomly oriented, discrete fibers that enhance isotropic mechanical properties, while long fiber reinforced rubber exhibits aligned, continuous fibers that provide superior strength and stiffness along the fiber direction. The microstructure of short fiber composites promotes uniform stress distribution and improved impact resistance, whereas long fiber composites offer enhanced load transfer efficiency and anisotropic behavior. Understanding these microstructural differences helps you select the optimal reinforcement type for specific performance requirements in rubber applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Short fiber reinforced rubber exhibits enhanced stiffness and improved wear resistance due to the high fiber content and uniform dispersion, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and durability. Long fiber reinforced rubber offers superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and elongation properties, attributed to the continuous fiber length that provides effective load transfer and resistance to crack propagation. Mechanical performance in long fiber composites typically surpasses short fiber counterparts, especially in dynamic loading and fatigue endurance scenarios.
Impact on Durability and Wear Resistance
Short fiber reinforced rubber enhances wear resistance by distributing stress uniformly across the matrix, reducing crack propagation and surface degradation. Long fiber reinforced rubber significantly improves durability through superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to mechanical fatigue, resulting in prolonged lifespan under high-stress applications. The fiber length directly influences the composite's ability to withstand abrasive forces and cyclic loading, with long fibers offering greater reinforcement for durability, while short fibers optimize resistance to surface wear.
Processing Methods and Manufacturing Considerations
Short fiber reinforced rubber typically utilizes injection molding or compression molding techniques, promoting uniform fiber dispersion and improved processability. Long fiber reinforced rubber demands specialized extrusion or pultrusion methods to maintain fiber integrity and orientation, enhancing mechanical performance but complicating manufacturing. Considerations include fiber length effects on viscosity, mold filling behavior, and the necessity for precise fiber alignment to optimize composite properties.
Typical Applications of Short vs Long Fiber Reinforced Rubber
Short fiber reinforced rubber is typically used in applications requiring enhanced wear resistance and dimensional stability, such as automotive engine mounts, seals, and vibration dampers. Long fiber reinforced rubber is preferred for high-performance applications demanding superior mechanical strength and fatigue resistance, including conveyor belts, industrial hoses, and pneumatic tires. Both types provide tailored reinforcement but differ significantly in load-bearing capabilities and flexibility.
Cost Implications and Economic Factors
Short fiber reinforced rubber generally offers lower material and processing costs due to easier mixing and shorter cycle times, making it more economical for high-volume production. Long fiber reinforced rubber provides superior mechanical properties but involves higher manufacturing complexity and costs, impacting the overall investment for your project. Balancing performance needs with budget constraints is crucial when choosing between these reinforcement types.
Future Trends and Advancements in Fiber Reinforced Rubber
Future trends in fiber reinforced rubber emphasize enhanced durability and performance through nanotechnology integration and hybrid fiber systems that combine short and long fibers for optimized strength and flexibility. Advancements in sustainable materials and smart fibers capable of self-sensing and self-healing properties are poised to transform your applications in automotive and aerospace industries. Improved manufacturing processes such as automated fiber alignment and 3D printing enable precise control over fiber distribution, driving innovation in tailored rubber composites.
Short fiber reinforced vs Long fiber reinforced rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com