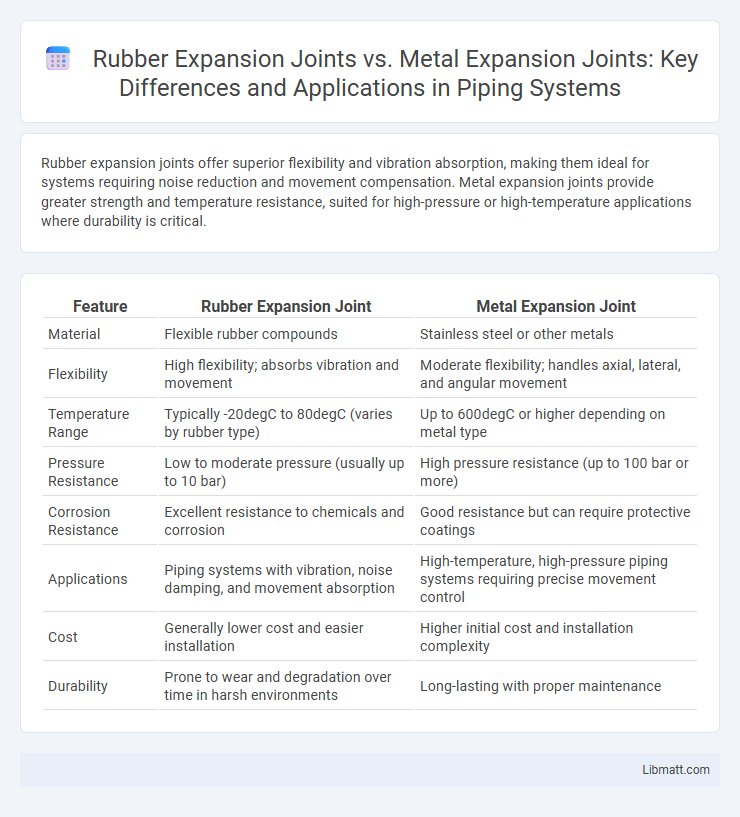
Rubber expansion joints offer superior flexibility and vibration absorption, making them ideal for systems requiring noise reduction and movement compensation. Metal expansion joints provide greater strength and temperature resistance, suited for high-pressure or high-temperature applications where durability is critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rubber Expansion Joint | Metal Expansion Joint |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Flexible rubber compounds | Stainless steel or other metals |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; absorbs vibration and movement | Moderate flexibility; handles axial, lateral, and angular movement |
| Temperature Range | Typically -20degC to 80degC (varies by rubber type) | Up to 600degC or higher depending on metal type |
| Pressure Resistance | Low to moderate pressure (usually up to 10 bar) | High pressure resistance (up to 100 bar or more) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and corrosion | Good resistance but can require protective coatings |
| Applications | Piping systems with vibration, noise damping, and movement absorption | High-temperature, high-pressure piping systems requiring precise movement control |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and easier installation | Higher initial cost and installation complexity |
| Durability | Prone to wear and degradation over time in harsh environments | Long-lasting with proper maintenance |
Introduction to Expansion Joints
Expansion joints are critical components used to absorb thermal expansion, vibrations, and movement in piping systems. Rubber expansion joints provide flexibility and excellent resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for applications involving chemicals or varying temperatures. Metal expansion joints offer high strength and durability in high-pressure or high-temperature environments, ensuring long-lasting performance in industrial settings.
Overview of Rubber Expansion Joints
Rubber expansion joints provide flexible connections that absorb vibrations, thermal movements, and mechanical noise in piping systems, enhancing durability and reducing stress on pipes and equipment. They are made from elastomeric materials combined with fabric reinforcements, offering excellent resistance to chemicals, temperature variations, and pressure fluctuations. These joints are widely used in HVAC systems, water treatment plants, and industrial applications where flexibility and corrosion resistance are essential.
Overview of Metal Expansion Joints
Metal expansion joints are engineered to absorb thermal expansion and mechanical vibration in piping systems, offering high strength and durability under extreme temperatures and pressures. Typically made from stainless steel or other alloy metals, these joints provide excellent resistance to corrosion and fatigue, making them suitable for industrial applications such as power plants, refineries, and chemical processing. Their ability to accommodate axial, lateral, and angular movements ensures reliable performance in dynamic environments where precision and long service life are critical.
Key Differences Between Rubber and Metal Expansion Joints
Rubber expansion joints provide superior flexibility and vibration absorption, making them ideal for applications requiring noise reduction and movement accommodation in piping systems. Metal expansion joints excel in high-temperature and high-pressure environments due to their durability and resistance to corrosion, offering long-term reliability in industrial settings. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate expansion joint for your system's operational needs and environmental conditions.
Applications of Rubber Expansion Joints
Rubber expansion joints are widely used in applications requiring vibration isolation, noise reduction, and accommodation of thermal expansion in piping systems across industries like HVAC, water treatment, and chemical processing. Their flexibility makes them ideal for absorbing lateral, axial, and angular movements in pipelines handling corrosive fluids or abrasive materials. Compared to metal expansion joints, rubber variants excel in systems where resistance to corrosion, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness are critical factors.
Applications of Metal Expansion Joints
Metal expansion joints are extensively used in high-temperature and high-pressure industrial applications such as power plants, chemical processing, and oil refineries where durability and resistance to corrosion and extreme conditions are critical. These joints effectively absorb thermal expansion, vibrations, and mechanical movements in pipelines conveying steam, gases, and aggressive fluids, ensuring system integrity and reducing maintenance costs. You benefit from their robustness and longevity in demanding environments, enabling reliable operation under harsh industrial conditions.
Comparative Performance and Durability
Rubber expansion joints excel in flexibility and vibration absorption, making them ideal for systems with frequent movements and thermal expansion variations, while metal expansion joints provide superior strength and resistance to high temperatures and pressure. Your choice depends on the operating environment; rubber joints typically last longer in corrosive or chemically aggressive settings, whereas metal joints are preferred for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Both types offer unique benefits, but evaluating factors like pressure, temperature, and media compatibility ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Cost Analysis: Rubber vs Metal Expansion Joints
Rubber expansion joints generally offer lower initial costs compared to metal expansion joints due to simpler manufacturing processes and cheaper raw materials like elastomers versus metals such as stainless steel. Maintenance expenses for rubber joints are typically lower since they resist vibration and noise better, reducing wear and tear, whereas metal joints often require regular inspection for corrosion and fatigue. Long-term cost efficiency favors rubber joints in applications with lower pressure and temperature, while metal joints, though more expensive upfront, provide durability and strength in high-temperature or high-pressure conditions, potentially reducing replacement frequency.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Rubber expansion joints offer easier installation due to their flexibility and lighter weight, reducing the need for precise alignment and heavy support structures compared to metal expansion joints. Maintenance of rubber joints typically involves regular inspection for cracking, swelling, or abrasion, with the possibility of cost-effective replacement, whereas metal expansion joints demand more rigorous monitoring for fatigue, corrosion, and weld integrity, often requiring specialized repairs. The choice impacts operational downtime, as rubber joints generally allow faster maintenance turnaround, enhancing overall system reliability.
Choosing the Right Expansion Joint for Your Project
Rubber expansion joints offer excellent flexibility, vibration absorption, and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for systems handling corrosive fluids or requiring noise reduction. Metal expansion joints provide higher pressure and temperature tolerance, making them suitable for high-temperature industrial applications with minimal movement requirements. Choosing the right expansion joint for your project depends on factors like operating temperature, pressure, chemical compatibility, and movement needs to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Rubber Expansion Joint vs Metal Expansion Joint Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com