Rubber extrusion involves shaping rubber compounds into continuous profiles by forcing them through a die, providing flexible, resilient products often used in seals and gaskets. Plastic extrusion, on the other hand, heats and pushes thermoplastic materials through a die to create rigid or flexible items like pipes and sheets, offering versatile applications with varying levels of durability and strength.
Table of Comparison
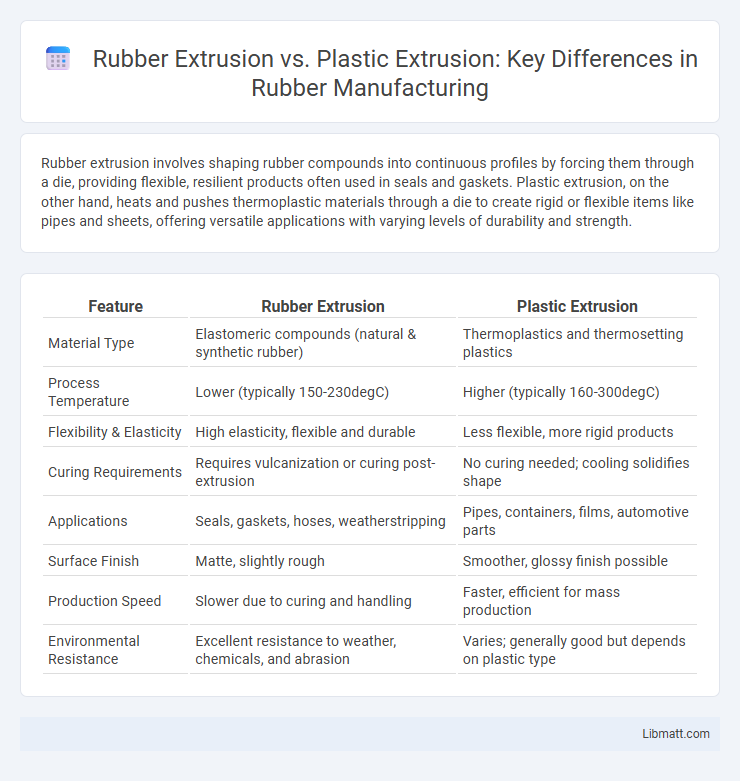
| Feature | Rubber Extrusion | Plastic Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Elastomeric compounds (natural & synthetic rubber) | Thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics |
| Process Temperature | Lower (typically 150-230degC) | Higher (typically 160-300degC) |
| Flexibility & Elasticity | High elasticity, flexible and durable | Less flexible, more rigid products |
| Curing Requirements | Requires vulcanization or curing post-extrusion | No curing needed; cooling solidifies shape |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, hoses, weatherstripping | Pipes, containers, films, automotive parts |
| Surface Finish | Matte, slightly rough | Smoother, glossy finish possible |
| Production Speed | Slower due to curing and handling | Faster, efficient for mass production |
| Environmental Resistance | Excellent resistance to weather, chemicals, and abrasion | Varies; generally good but depends on plastic type |
Introduction to Rubber vs Plastic Extrusion
Rubber extrusion involves shaping heated rubber material by forcing it through a die, producing flexible, elastic products like seals and gaskets, while plastic extrusion shapes melted plastic pellets into rigid or semi-flexible forms such as pipes and profiles. The key difference lies in the material properties and processing temperatures; rubber requires controlled vulcanization post-extrusion, whereas plastic extrusion solidifies as it cools. Choosing between rubber and plastic extrusion depends on application needs for elasticity, durability, and environmental resistance.
Key Differences in Extrusion Processes
Rubber extrusion involves forcing uncured rubber compounds through a shaped die followed by vulcanization, which chemically cures the material to enhance elasticity and durability, whereas plastic extrusion melts plastic pellets that solidify upon cooling without chemical curing. Rubber extrusion typically requires precise temperature and pressure control to maintain compound properties, while plastic extrusion focuses on managing melt flow and cooling rates for dimensional accuracy. The inherent differences in thermal and chemical processing between rubber and plastic extrusion dictate distinct equipment designs and operational parameters.
Material Properties Comparison
Rubber extrusion offers superior elasticity, resilience, and resistance to extreme temperatures compared to plastic extrusion, which typically provides higher rigidity and structural stability. Your choice depends on the application's need for flexibility, with rubber excelling in sealing and vibration damping, while plastic is preferred for lightweight, durable parts. Material properties such as tensile strength, elongation, and environmental resistance play a critical role in deciding between these two extrusion methods.
Common Applications of Rubber Extrusion
Rubber extrusion is commonly used in automotive seals, weatherstripping, and vibration dampening components due to its flexibility and resistance to environmental factors. Industries such as construction and electronics rely on rubber extrusions for gasket production, tubing, and protective covers. Unlike plastic extrusion, rubber extrusion excels in applications requiring elasticity and durability under varying temperatures.
Common Applications of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is widely used for creating pipes, tubing, weatherstripping, and window frames, thanks to its ability to produce long, continuous shapes with consistent cross-sections. You can also find plastic extrusion in the manufacture of cable insulation, automotive trim, and packaging films, where durability and flexibility are essential. This process supports high-volume production with precise control over material properties, making it ideal for everyday consumer and industrial products.
Advantages of Rubber Extrusion
Rubber extrusion offers superior elasticity and flexibility compared to plastic extrusion, making it ideal for applications requiring durable seals, gaskets, and vibration dampening. Its ability to maintain performance under extreme temperatures and resist abrasion, weathering, and chemicals provides long-lasting reliability in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors. The process accommodates complex profiles and tight tolerances, enhancing product functionality and reducing the need for secondary operations.
Advantages of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion offers superior versatility in producing complex shapes with high precision and consistency, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing. It provides excellent material efficiency and cost-effectiveness due to faster cycle times and recyclability of waste. Your production will benefit from enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors, unlike rubber extrusion which may have limitations in these areas.
Challenges and Limitations
Rubber extrusion faces challenges such as maintaining consistent material properties and managing higher processing temperatures compared to plastic extrusion, which often deals with lower melting points but requires precise control to prevent warping and shrinkage. Your production may encounter limitations in rubber extrusion due to the material's elasticity and longer curing times, whereas plastic extrusion limitations include sensitivity to moisture and the need for exact temperature profiles to ensure product integrity. Both processes demand specialized equipment and expertise to overcome issues related to die swelling, surface finish, and dimensional stability.
Cost Considerations
Rubber extrusion generally incurs higher material costs due to the specialized compounds required, while plastic extrusion benefits from a broader range of affordable thermoplastic resins. Your choice impacts tooling expenses, as rubber extrusion often demands more complex dies to accommodate its elasticity, increasing initial investment compared to plastic extrusion. Long-term production costs favor plastic extrusion with faster cycle times and easier reprocessing, making it a cost-effective solution for high-volume manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Extrusion Method for Your Project
Rubber extrusion and plastic extrusion each offer unique advantages depending on material properties and project requirements. Rubber extrusion excels in flexibility, sealing, and shock absorption, ideal for gaskets and weatherstripping, while plastic extrusion suits rigid, durable components like pipes and profiles. Evaluating factors such as temperature resistance, elasticity, and environmental exposure ensures you select the right extrusion method for your project's performance and longevity.
Rubber Extrusion vs Plastic Extrusion Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com