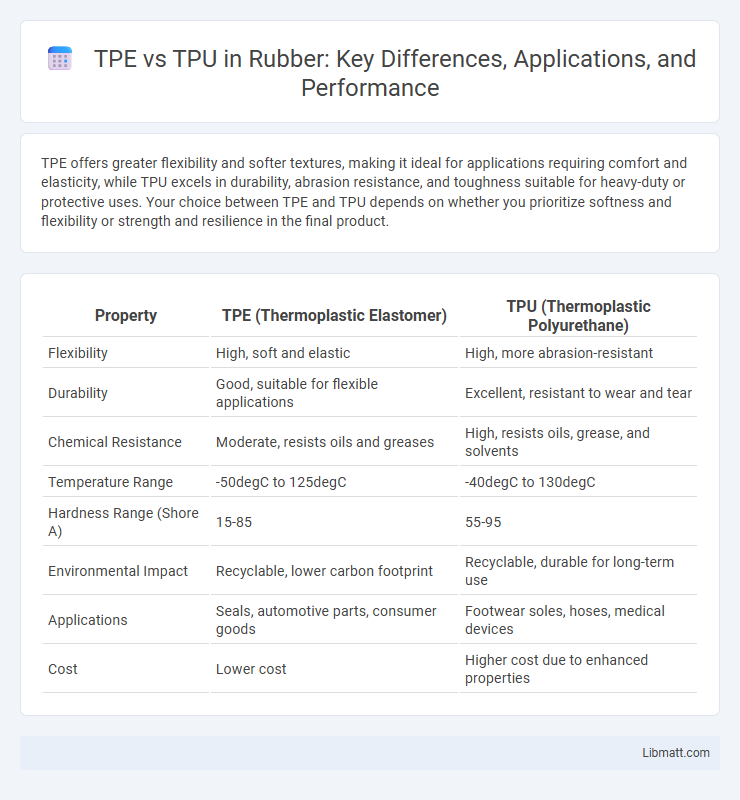
TPE offers greater flexibility and softer textures, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and elasticity, while TPU excels in durability, abrasion resistance, and toughness suitable for heavy-duty or protective uses. Your choice between TPE and TPU depends on whether you prioritize softness and flexibility or strength and resilience in the final product.
Table of Comparison
| Property | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) | TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High, soft and elastic | High, more abrasion-resistant |
| Durability | Good, suitable for flexible applications | Excellent, resistant to wear and tear |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, resists oils and greases | High, resists oils, grease, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 125degC | -40degC to 130degC |
| Hardness Range (Shore A) | 15-85 | 55-95 |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower carbon footprint | Recyclable, durable for long-term use |
| Applications | Seals, automotive parts, consumer goods | Footwear soles, hoses, medical devices |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to TPE vs TPU
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are versatile materials combining the properties of rubber with the processability of plastics, widely used for flexible and durable products. Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) are a subset of TPEs known for superior abrasion resistance, elasticity, and transparency, commonly applied in footwear, automotive parts, and medical devices. Comparing TPE and TPU highlights TPU's enhanced mechanical properties and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
What is TPE?
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) are a class of polymers combining the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastics, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability. TPE materials offer excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and temperature variations, which contributes to their widespread use in automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods. Unlike Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), TPEs typically provide softer tactile properties and easier moldability for diverse manufacturing processes.
What is TPU?
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a highly versatile elastomer known for its excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and high tensile strength, making it ideal for applications in footwear, automotive parts, and protective cases. TPU balances the properties of rubber and plastic, offering superior durability and elasticity compared to Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE). Its unique chemical structure allows TPU to withstand extreme temperatures and resist oil, grease, and corrosion, which enhances product longevity and performance.
Key Differences Between TPE and TPU
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) offers greater flexibility and softer texture, making it ideal for applications requiring elasticity and comfort, while TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) provides superior abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and durability for high-performance uses. TPE is generally more cost-effective and easier to process, whereas TPU exhibits higher tensile strength and better resilience under harsh conditions. Key differences lie in their mechanical properties, with TPU excelling in toughness and TPE favored for softness and formability.
Material Properties Comparison
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) offers excellent flexibility, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for applications requiring soft touch and durability. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) combines high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and superior chemical resistance, providing enhanced durability in demanding environments. Both materials exhibit good elasticity, but TPU generally outperforms TPE in strength and resistance to oils and solvents, while TPE excels in softness and ease of processing.
Common Applications for TPE
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) is widely used in consumer goods, automotive parts, medical devices, and flexible packaging due to its flexibility, durability, and ease of processing. Industries often choose TPE for items like soft-touch grips, seals, tubing, and toys because it combines the properties of rubber with the recyclability of plastics. Your selection of TPE ensures cost-effective production and excellent performance in applications requiring elasticity and resistance to environmental factors.
Common Applications for TPU
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is widely used in industries requiring flexibility and durability, such as automotive parts, sports equipment, and medical devices. TPU's excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity make it ideal for protective phone cases, footwear soles, and flexible tubing. Its chemical resistance and transparency also suit applications like inflatable rafts, film packaging, and 3D printing filaments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TPE
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer excellent flexibility, recyclability, and processability, making them ideal for applications that require repeated flexing and bending, such as automotive parts and medical devices. TPE materials provide superior resistance to impact and chemicals but generally have lower tensile strength and heat resistance compared to thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). While TPE is cost-effective and environmentally friendly due to its recyclability, it may lack the abrasion resistance and durability needed for heavy-duty applications where TPU typically excels.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TPU
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) offers high abrasion resistance, flexibility, and excellent elasticity, making it ideal for protective cases, footwear, and industrial applications. However, TPU can be more expensive and less UV resistant compared to Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE), which may limit its use in prolonged outdoor exposure. Your choice of TPU ensures durability and strength but might require additional treatments or coatings to enhance weather resistance.
How to Choose Between TPE and TPU
Choosing between TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) depends on application-specific requirements such as flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance. TPE offers superior softness and elasticity ideal for products requiring comfort, while TPU excels in abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and tensile strength for more demanding industrial uses. Assess factors like operating temperature, wear conditions, and exposure to oils or UV light to determine the optimal material for your project.
TPE vs TPU Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com