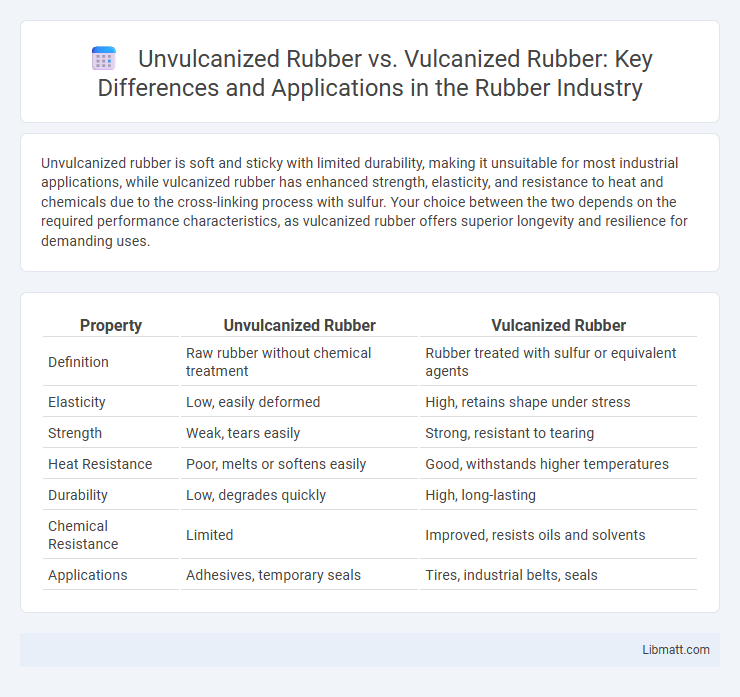
Unvulcanized rubber is soft and sticky with limited durability, making it unsuitable for most industrial applications, while vulcanized rubber has enhanced strength, elasticity, and resistance to heat and chemicals due to the cross-linking process with sulfur. Your choice between the two depends on the required performance characteristics, as vulcanized rubber offers superior longevity and resilience for demanding uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Unvulcanized Rubber | Vulcanized Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw rubber without chemical treatment | Rubber treated with sulfur or equivalent agents |
| Elasticity | Low, easily deformed | High, retains shape under stress |
| Strength | Weak, tears easily | Strong, resistant to tearing |
| Heat Resistance | Poor, melts or softens easily | Good, withstands higher temperatures |
| Durability | Low, degrades quickly | High, long-lasting |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited | Improved, resists oils and solvents |
| Applications | Adhesives, temporary seals | Tires, industrial belts, seals |
Introduction to Rubber: Unvulcanized vs Vulcanized
Unvulcanized rubber is raw natural or synthetic rubber that remains soft, sticky, and highly elastic without any chemical cross-linking. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical process involving sulfur or other curatives that create cross-links between polymer chains, enhancing durability, elasticity, and heat resistance. This transformation improves mechanical properties, making vulcanized rubber ideal for tires, seals, and industrial products compared to the less stable unvulcanized form.
Understanding the Vulcanization Process
The vulcanization process transforms unvulcanized rubber, a sticky and pliable material, into a durable and elastic product by heating it with sulfur or other curatives. This chemical reaction creates cross-links between polymer chains, enhancing the rubber's strength, resilience, and resistance to heat, chemicals, and wear. Understanding this process helps you select the right type of rubber for applications requiring improved mechanical performance and longevity.
Key Differences in Chemical Structure
Unvulcanized rubber consists of long polymer chains that are loosely entangled without cross-linking, resulting in a softer and more elastic material susceptible to deformation. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical process introducing sulfur cross-links between polymer chains, significantly enhancing its strength, elasticity, and resistance to heat and chemicals. The presence of these sulfur cross-links in vulcanized rubber transforms its molecular structure from linear to a three-dimensional network, providing improved durability and stability compared to unvulcanized rubber.
Physical Properties Comparison
Unvulcanized rubber is soft, sticky, and lacks elasticity, making it prone to deformation and low mechanical strength, whereas vulcanized rubber undergoes cross-linking through sulfur or other curatives, resulting in enhanced hardness, resilience, and resistance to abrasion and temperature changes. Your choice between the two affects durability, with vulcanized rubber offering superior tensile strength and elasticity, suitable for demanding applications. The vulcanization process significantly improves chemical stability and wear resistance, critical for industrial and automotive uses.
Durability and Strength
Unvulcanized rubber exhibits lower durability and tensile strength, making it more susceptible to wear, deformation, and environmental damage over time. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical process involving sulfur cross-linking, significantly enhancing its mechanical properties, including higher tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion. This cross-linking structure in vulcanized rubber provides superior durability and performance for industrial applications compared to the softer, less resilient unvulcanized rubber.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Unvulcanized rubber maintains higher flexibility and elasticity due to its untreated polymer chains, allowing it to stretch easily but with weaker mechanical strength. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a sulfur cross-linking process, which significantly enhances its elasticity by providing improved resilience and shape retention under stress. This curing process transforms the rubber into a more durable material with reduced flexibility but superior elastic recovery, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term performance.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
Unvulcanized rubber is primarily used in temporary or low-stress applications such as adhesives, sealants, and cushioning materials due to its softness and flexibility. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical process that significantly enhances its durability, heat resistance, and mechanical strength, making it essential for high-performance industrial products including tires, conveyor belts, hoses, and seals. Your choice between these materials depends on the required longevity, performance under stress, and exposure to environmental conditions in commercial and industrial settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Unvulcanized rubber is more biodegradable due to its natural composition, allowing for easier decomposition and less environmental persistence. Vulcanized rubber, treated with sulfur and other chemicals during sulfur vulcanization, becomes more durable but less eco-friendly because it resists degradation and contributes significantly to landfill waste. For your sustainability goals, choosing unvulcanized rubber can reduce environmental impact by promoting a more circular lifecycle in rubber products.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Factors
Unvulcanized rubber typically offers lower initial costs due to less processing, making it economical for short-term applications or products with a limited lifespan. Vulcanized rubber, while more expensive upfront because of the additional heat and sulfur treatment, provides superior durability and resilience, reducing long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Considering your project's lifecycle and performance needs helps determine the most cost-effective choice between these rubber types.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Unvulcanized rubber offers flexibility and ease of processing, making it ideal for temporary applications and prototyping where reshaping is frequently needed. Vulcanized rubber provides enhanced durability, heat resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for long-term uses in automotive tires, industrial seals, and footwear soles. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing the need for flexibility versus longevity and performance under stress or environmental exposure.
Unvulcanized Rubber vs Vulcanized Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com