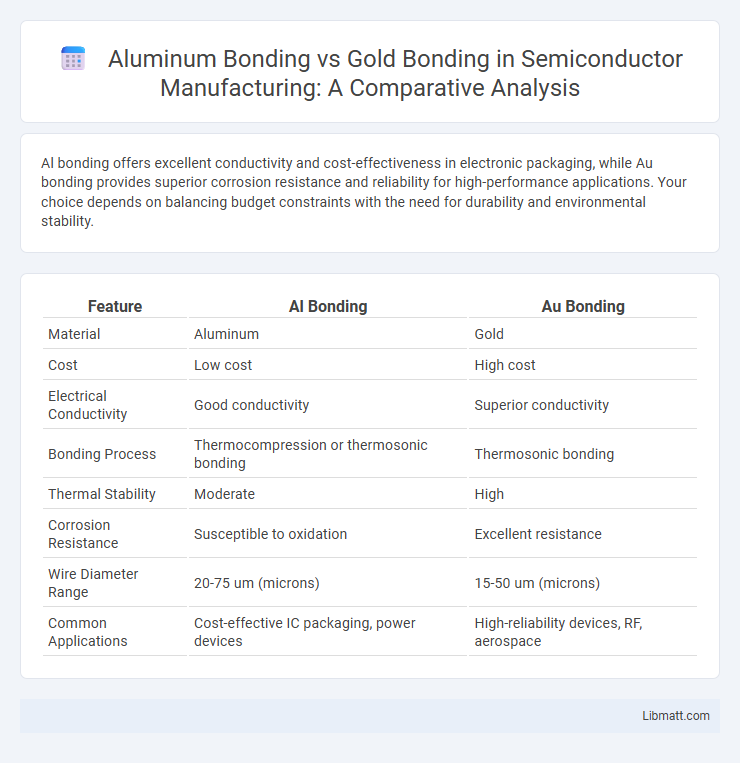
Al bonding offers excellent conductivity and cost-effectiveness in electronic packaging, while Au bonding provides superior corrosion resistance and reliability for high-performance applications. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for durability and environmental stability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Al Bonding | Au Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum | Gold |
| Cost | Low cost | High cost |
| Electrical Conductivity | Good conductivity | Superior conductivity |
| Bonding Process | Thermocompression or thermosonic bonding | Thermosonic bonding |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Susceptible to oxidation | Excellent resistance |
| Wire Diameter Range | 20-75 um (microns) | 15-50 um (microns) |
| Common Applications | Cost-effective IC packaging, power devices | High-reliability devices, RF, aerospace |
Introduction to Wire Bonding Technologies
Wire bonding technologies primarily utilize aluminum (Al) and gold (Au) for creating electrical interconnections in semiconductor devices. Aluminum bonding offers cost efficiency and excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for high-volume, low-frequency applications, while gold bonding provides superior corrosion resistance and better electrical performance in harsh environments. Selecting between Al and Au bonding depends on factors like application requirements, reliability standards, and manufacturing budget constraints.
Overview of Al Bonding
Al bonding involves using aluminum wire to create electrical connections in semiconductor devices, offering cost-effective conductivity and reliable performance in integrated circuits. Its lightweight nature and resistance to oxidation make aluminum bonding ideal for high-volume manufacturing and applications requiring stable metallurgical properties. Compared to gold bonding, aluminum bonding provides a notable advantage in terms of material cost while maintaining sufficient electrical and thermal conductivity for most microelectronic devices.
Overview of Au Bonding
Au bonding offers excellent electrical conductivity and superior corrosion resistance compared to Al bonding, making it ideal for high-reliability semiconductor connections. Gold's malleability and stable chemical properties ensure consistent performance in harsh environments, minimizing the risk of bond failure. Its widespread use in aerospace and medical device applications underscores its importance where long-term durability and precision are critical.
Material Properties: Al vs Au
Aluminum bonding offers lower electrical conductivity and a higher melting point (660degC) compared to gold's superior conductivity and melting point of 1064degC, influencing heat dissipation and reliability in microelectronics. Aluminum's natural oxide layer provides excellent corrosion resistance but can introduce challenges in wire bonding processes, whereas gold's inertness ensures stable, defect-free bonds with minimal oxidation. Cost-effectiveness and mechanical strength also differ, with aluminum being lighter and more economical, while gold provides enhanced ductility and resistance to mechanical deformation.
Applications of Al and Au Bonding
Al bonding is widely used in semiconductor packaging for microelectronic devices due to its excellent electrical conductivity, cost-effectiveness, and good thermal performance, making it ideal for power devices and integrated circuits. Au bonding is preferred in high-reliability applications such as aerospace, medical devices, and high-frequency components because of its superior corrosion resistance, ductility, and stable electrical properties. Your choice between Al and Au bonding depends on the specific environmental conditions, performance requirements, and budget constraints of your application.
Process Differences: Al vs Au
Al bonding uses thermosonic wedge bonding involving ultrasonic energy and heat to create a metallurgical bond, typically on aluminum pads with aluminum wire, ensuring strong intermetallic formation. Au bonding employs thermocompression or thermosonic ball bonding, primarily bonding gold wires to gold or palladium-plated pads, leveraging gold's superior malleability and oxidation resistance for reliable connections. The differences in process parameters, such as temperature ranges (Al bonding around 150-200degC and Au bonding between 250-350degC) and ultrasonic energy levels, reflect the distinct metallurgical properties of aluminum and gold materials.
Reliability and Performance Comparison
Al bonding offers superior reliability in high-temperature environments due to its excellent oxidation resistance and stable intermetallic formation, making it ideal for power electronics. Au bonding provides better electrical performance with lower contact resistance and is less prone to corrosion, enhancing signal integrity in precision devices. Both materials excel in wire bonding, but Al bonding is preferred for large-scale, cost-effective applications while Au bonding is favored for critical, high-frequency circuits requiring enhanced conductivity and durability.
Cost Analysis: Al Bonding vs Au Bonding
Al bonding offers a significantly lower cost compared to Au bonding due to the abundance and affordability of aluminum versus gold, making it a preferred choice for high-volume semiconductor manufacturing. While gold bonding provides superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, its high material cost and limited availability increase overall production expenses. Your decision depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements, where aluminum bonding can reduce costs without substantially compromising reliability in many applications.
Industry Trends and Innovations
Al bonding remains prevalent in microelectronics due to its cost efficiency and compatibility with silicon substrates, supporting mass production trends in consumer electronics. Au bonding, favored for its superior conductivity and corrosion resistance, drives innovations in high-performance applications such as aerospace and medical devices. Emerging hybrid bonding techniques integrate Al and Au properties, enhancing reliability and enabling the miniaturization required in next-generation semiconductor packaging.
Choosing the Right Bonding for Your Application
Aluminum (Al) bonding offers cost-effective performance with excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-volume semiconductor packaging and power devices, while gold (Au) bonding provides superior corrosion resistance and reliable connections in harsh environments or high-frequency circuits. Selecting the right bonding material depends on factors like operating temperature, electrical requirements, and environmental conditions. You should evaluate your application's thermal and mechanical stress tolerance to determine whether Al bonding's affordability or Au bonding's durability best suits your needs.
Al Bonding vs Au Bonding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com