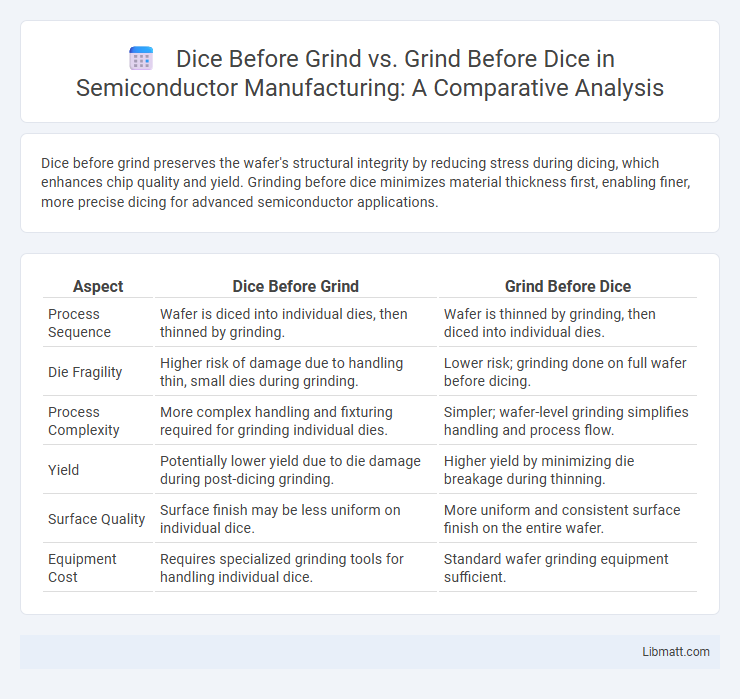
Dice before grind preserves the wafer's structural integrity by reducing stress during dicing, which enhances chip quality and yield. Grinding before dice minimizes material thickness first, enabling finer, more precise dicing for advanced semiconductor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dice Before Grind | Grind Before Dice |
|---|---|---|
| Process Sequence | Wafer is diced into individual dies, then thinned by grinding. | Wafer is thinned by grinding, then diced into individual dies. |
| Die Fragility | Higher risk of damage due to handling thin, small dies during grinding. | Lower risk; grinding done on full wafer before dicing. |
| Process Complexity | More complex handling and fixturing required for grinding individual dies. | Simpler; wafer-level grinding simplifies handling and process flow. |
| Yield | Potentially lower yield due to die damage during post-dicing grinding. | Higher yield by minimizing die breakage during thinning. |
| Surface Quality | Surface finish may be less uniform on individual dice. | More uniform and consistent surface finish on the entire wafer. |
| Equipment Cost | Requires specialized grinding tools for handling individual dice. | Standard wafer grinding equipment sufficient. |
Introduction to Knife Cutting Techniques
Knife cutting techniques vary significantly between dice before grind and grind before dice methods, each impacting texture and flavor extraction in culinary preparations. Dice before grind involves chopping ingredients into uniform cubes prior to grinding, preserving structural integrity and creating a distinct mouthfeel, ideal for dishes requiring precise texture. Conversely, grind before dice pulverizes ingredients first, resulting in finer, more homogenous mixtures that enhance flavor blending and are suited for emulsified or processed foods.
Understanding "Dice Before Grind" Method
The "Dice Before Grind" method involves cutting a wafer into individual dies prior to thinning or grinding, ensuring precise separation and reducing the risk of damage during the grinding process. This technique enhances yield by preventing chipping and cracking on die edges, which is critical for maintaining the structural integrity of microelectronic components. Understanding Your wafer processing requirements helps determine if the Dice Before Grind approach is optimal for maximizing device performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Exploring the "Grind Before Dice" Technique
The "Grind Before Dice" technique involves refining the surface of the material prior to precise dicing, resulting in smoother edges and minimized chipping during the cutting process. This method enhances the overall structural integrity of the diced components, making it particularly beneficial for delicate substrates used in semiconductor manufacturing. By optimizing material hardness and surface uniformity before dicing, manufacturers achieve higher yield rates and improved device performance in electronic assemblies.
Key Differences Between the Two Methods
Dice Before Grind involves cutting semiconductor wafers into individual chips prior to thinning, enabling precise alignment during grinding but increasing the risk of chip damage. Grind Before Dice thins the entire wafer first, improving wafer stability and reducing mechanical stress, which can enhance yield and minimize micro-cracks. Your choice between these methods should factor in device fragility, desired throughput, and overall process control requirements.
Impact on Food Texture and Consistency
Dice before grind preserves larger particle size in the final mixture, resulting in a coarser, chunkier texture that enhances mouthfeel in dishes like sausages or meatloaf. Grind before dice produces a finer, more uniform consistency by breaking down fibers early, which is ideal for smooth spreads or emulsified products. Texture and consistency are directly influenced by the sequence, affecting moisture retention, binding, and overall bite quality in culinary applications.
Efficiency and Speed: Which Saves Time?
Grinding before dicing generally saves time by reducing the wafer thickness, which simplifies the sawing process and minimizes blade wear, leading to faster cuts and improved throughput. Dice before grind can be less efficient as it requires careful handling of thicker substrates during dicing, increasing the risk of chipping and slower cutting speeds. Overall, grind before dice is favored for higher efficiency and speed in semiconductor wafer processing.
Best Applications for Each Technique
Dice Before Grind is best suited for applications requiring precise die separation before wafer thinning, such as advanced semiconductor packaging and MEMS devices where maintaining die integrity is critical. Grind Before Dice excels in high-volume manufacturing environments, especially for standard ICs, as it streamlines wafer thinning while preserving wafer strength during dicing. Your choice between these techniques depends on balancing production efficiency and the sensitivity of the die structure.
Tips for Choosing the Right Method
Choosing between dice before grind and grind before dice depends on your recipe and desired texture; dicing first preserves the firmness of ingredients, ideal for stir-fries or salads. Grinding beforehand works best for uniform mixing in dishes like meatloafs or spreads, creating a consistent texture throughout. Consider your cooking method and ingredient type to ensure your preparation aligns with your dish's flavor and presentation goals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes to avoid when choosing between Dice Before Grind and Grind Before Dice include neglecting the material properties and final texture requirements, which can lead to suboptimal cutting performance or premature wear. Failing to account for the specific tool geometry and cutting conditions may result in improper chip formation and reduced tool life. Ensure Your process selection aligns with the desired precision and surface finish to prevent costly rework or tool failure.
Conclusion: Finding the Ideal Cutting Sequence
Choosing between Dice Before Grind and Grind Before Dice depends on the specific application requirements, including target die size, wafer thickness, and stress tolerance. Dice Before Grind is ideal for delicate, ultra-thin wafers as it minimizes mechanical stress during dicing, whereas Grind Before Dice offers better precision for thicker wafers by enabling uniform thickness before cutting. Optimizing the cutting sequence enhances yield and device reliability by balancing process efficiency and wafer integrity.
Dice Before Grind vs Grind Before Dice Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com