Die attach offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical stability compared to wire bond, making it ideal for high-power applications where heat dissipation and reliability are critical. Your choice depends on the specific requirements of your device, as wire bonding provides greater flexibility for complex interconnections but may limit thermal performance.
Table of Comparison
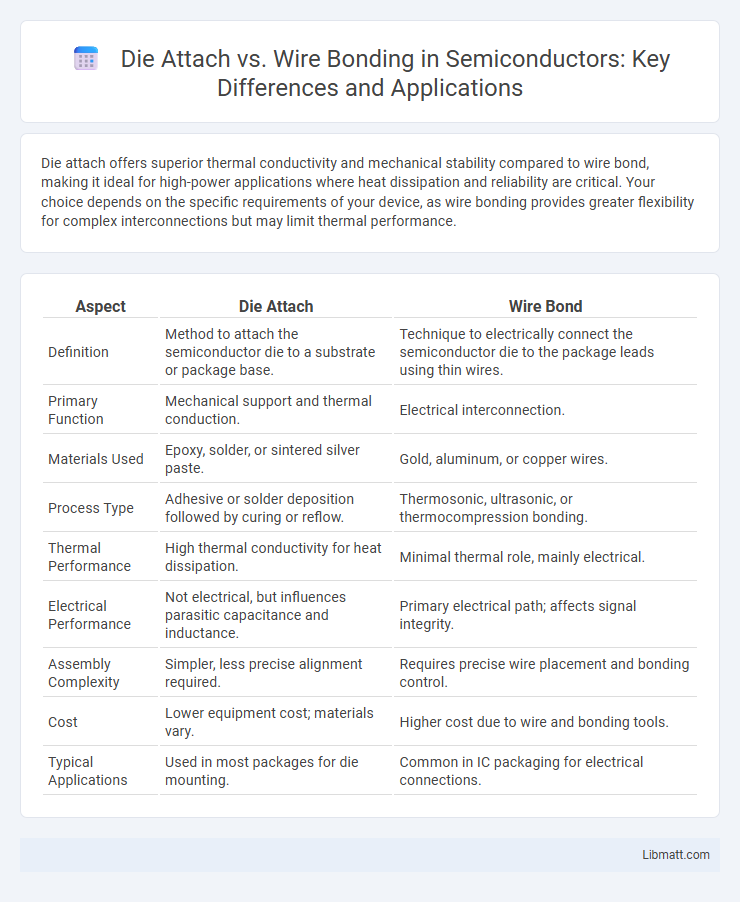
| Aspect | Die Attach | Wire Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Method to attach the semiconductor die to a substrate or package base. | Technique to electrically connect the semiconductor die to the package leads using thin wires. |
| Primary Function | Mechanical support and thermal conduction. | Electrical interconnection. |
| Materials Used | Epoxy, solder, or sintered silver paste. | Gold, aluminum, or copper wires. |
| Process Type | Adhesive or solder deposition followed by curing or reflow. | Thermosonic, ultrasonic, or thermocompression bonding. |
| Thermal Performance | High thermal conductivity for heat dissipation. | Minimal thermal role, mainly electrical. |
| Electrical Performance | Not electrical, but influences parasitic capacitance and inductance. | Primary electrical path; affects signal integrity. |
| Assembly Complexity | Simpler, less precise alignment required. | Requires precise wire placement and bonding control. |
| Cost | Lower equipment cost; materials vary. | Higher cost due to wire and bonding tools. |
| Typical Applications | Used in most packages for die mounting. | Common in IC packaging for electrical connections. |
Introduction to Die Attach and Wire Bond
Die attach involves securing the semiconductor die to the substrate using adhesives or solder, providing mechanical support and thermal conductivity essential for device performance. Wire bonding connects the die's pads to the package leads with fine wires, enabling electrical signal transmission and influencing reliability and signal integrity. Understanding the differences in materials, processes, and applications between die attach and wire bond is crucial for optimizing your semiconductor assembly.
Understanding Die Attach Technology
Die attach technology plays a crucial role in semiconductor packaging by securely mounting the die onto the substrate, ensuring thermal conductivity and mechanical stability. Unlike wire bond methods that create electrical interconnections through fine wires, die attach focuses primarily on the physical and thermal interface between the die and package. Choosing the right die attach material and process directly impacts the performance, reliability, and heat dissipation capabilities of your electronic device.
Wire Bonding: Fundamentals and Process
Wire bonding is a microelectronic interconnection technique that uses fine metal wires, typically gold or aluminum, to electrically connect semiconductor chips to their packaging substrates. The process involves ultrasonic or thermosonic bonding methods to create strong, reliable joints between bond pads on the die and the lead frame or substrate, ensuring signal integrity and mechanical stability. Mastering wire bonding fundamentals allows you to optimize device performance, enhance manufacturing yield, and meet stringent reliability standards.
Key Differences Between Die Attach and Wire Bond
Die attach and wire bond are critical semiconductor packaging techniques, each serving distinct purposes in device assembly. Die attach involves affixing the semiconductor die directly to the package or substrate, providing mechanical support and thermal conductivity, while wire bond connects the die's bonding pads to the package leads through fine wires to establish electrical connections. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your device performance by selecting die attach for structural stability and wire bond for efficient signal transmission.
Applications of Die Attach in Semiconductor Packaging
Die attach serves as a critical method for mounting semiconductor chips to substrates or lead frames, providing mechanical support, thermal conduction, and electrical connectivity. It is widely utilized in power devices, LEDs, and multichip modules where efficient heat dissipation and robust mechanical stability are essential. This technique is favored in applications requiring high reliability and enhanced thermal management, such as automotive electronics and high-frequency RF components.
Common Uses of Wire Bonding in Electronics
Wire bonding is extensively used in semiconductor packaging to establish electrical connections between the integrated circuit (IC) and the external leads of its package, making it essential for microchips in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and medical devices. Unlike die attach, which focuses on physically securing the die to the substrate, wire bonding ensures reliable electrical pathways through fine gold or aluminum wires, enabling high-density interconnects. Your choice of wire bonding accommodates cost-effective, scalable manufacturing for devices such as sensors, microprocessors, and RF components.
Comparative Advantages: Die Attach vs Wire Bond
Die attach offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical stability, making it ideal for high-power and high-reliability applications, while wire bonding provides greater design flexibility and cost efficiency in complex integrated circuits. Die attach techniques reduce parasitic inductance and resistance, enhancing electrical performance, whereas wire bonding excels in fine-pitch interconnects and rapid prototyping. Selecting between die attach and wire bond depends on application-specific requirements such as heat dissipation, space constraints, and production volume.
Challenges in Die Attach and Wire Bond Processes
Challenges in die attach processes include ensuring precise alignment and strong mechanical adhesion between the die and substrate, which affects thermal conductivity and electrical performance. Wire bond processes face difficulties such as achieving reliable bond quality on various metallizations and managing loop formation to prevent wire sweep and shorts during encapsulation. Your manufacturing yield can be significantly impacted by controlling these critical parameters in both die attach and wire bonding techniques.
Advancements in Die Attach and Wire Bonding Techniques
Advancements in die attach techniques include the development of anisotropic conductive adhesives and sintered silver pastes, enabling improved thermal conductivity and mechanical strength for high-power semiconductor devices. Wire bonding innovations focus on ultrasonic and thermosonic bonding methods, offering enhanced bond reliability and finer pitch capability for advanced integrated circuits. Both fields benefit from automation and in-line inspection technologies, significantly increasing manufacturing precision and yield.
Choosing the Right Method: Die Attach or Wire Bond?
Choosing between die attach and wire bond depends on factors such as thermal performance, electrical conductivity, and assembly complexity. Die attach offers superior thermal management and mechanical strength by directly bonding the die to the substrate, making it ideal for high-power applications. Wire bond provides flexibility in connecting multiple pads and is cost-effective for low to medium volume semiconductor packaging, often used in fine-pitch devices.
Die Attach vs Wire Bond Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com