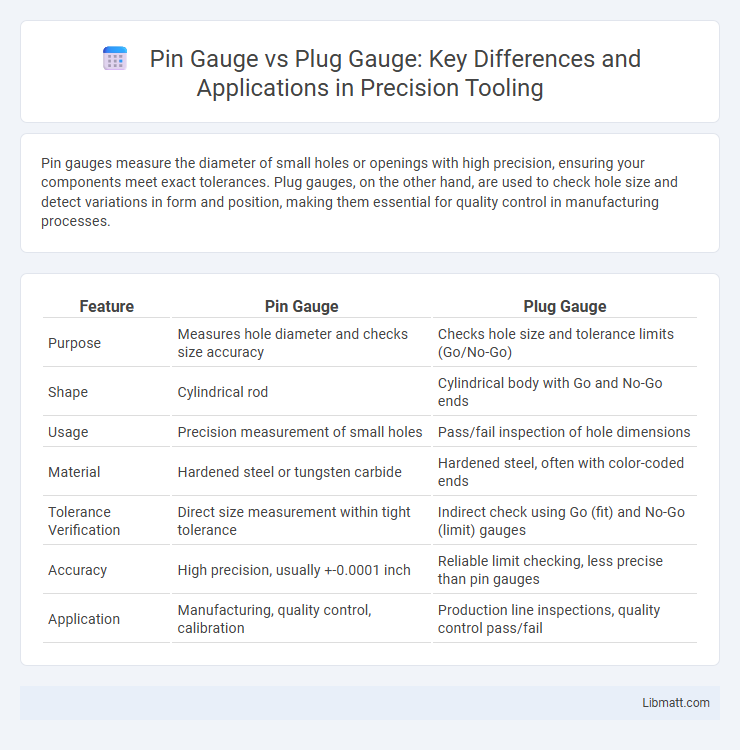
Pin gauges measure the diameter of small holes or openings with high precision, ensuring your components meet exact tolerances. Plug gauges, on the other hand, are used to check hole size and detect variations in form and position, making them essential for quality control in manufacturing processes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pin Gauge | Plug Gauge |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures hole diameter and checks size accuracy | Checks hole size and tolerance limits (Go/No-Go) |
| Shape | Cylindrical rod | Cylindrical body with Go and No-Go ends |
| Usage | Precision measurement of small holes | Pass/fail inspection of hole dimensions |
| Material | Hardened steel or tungsten carbide | Hardened steel, often with color-coded ends |
| Tolerance Verification | Direct size measurement within tight tolerance | Indirect check using Go (fit) and No-Go (limit) gauges |
| Accuracy | High precision, usually +-0.0001 inch | Reliable limit checking, less precise than pin gauges |
| Application | Manufacturing, quality control, calibration | Production line inspections, quality control pass/fail |
Introduction to Pin Gauges and Plug Gauges
Pin gauges are precision cylindrical tools used to measure hole diameters and test the accuracy of small apertures in manufacturing, ensuring tight tolerance verification. Plug gauges, typically composed of a handle and a gauging head, serve to inspect the internal dimensions of holes, verifying both minimum and maximum size limits for quality control. Both gauges are essential for maintaining dimensional accuracy in machining and assembly processes.
Defining Pin Gauges: Key Features and Applications
Pin gauges are precision measuring tools used to check hole diameters and ensure tight tolerance fits by verifying the size of small holes or slots with high accuracy. Constructed from hardened steel or carbide, pin gauges come in various sizes and are essential in quality control for manufacturing processes to maintain dimensional accuracy. You can rely on pin gauges for applications requiring consistent hole size measurements, such as in machining, automotive, and aerospace industries.
Understanding Plug Gauges: Functions and Types
Plug gauges are precision measuring tools used to check the internal dimensions of holes, ensuring they meet specified tolerances. Common types include go/no-go gauges, which verify whether a hole diameter is within acceptable limits, and setting plugs that calibrate other measuring instruments. These gauges play a critical role in quality control across manufacturing industries by guaranteeing the accuracy and consistency of hole sizes.
Pin Gauge vs Plug Gauge: Core Differences
Pin gauge measures small hole diameters with precise cylindrical pins to verify inner dimensions, while plug gauge combines a go/no-go feature using a solid, often stepped cylindrical design to ensure hole tolerances. Pin gauges provide high accuracy for inspection of fine internal dimensions in manufacturing and assembly processes, whereas plug gauges offer quick pass/fail verification for hole size conformity. The core difference lies in pin gauges measuring exact diameters and plug gauges testing acceptance criteria for hole size limits.
Accuracy and Precision Comparison
Pin gauges provide higher accuracy for measuring small hole diameters due to their fixed, calibrated sizes, ensuring precise verification of hole dimensions. Plug gauges offer reliable precision in go/no-go testing by assessing whether a hole meets specified tolerances without quantifying exact measurements. The choice between pin and plug gauges depends on the required measurement detail, with pin gauges favored for exact diameter verification and plug gauges for tolerance checking.
Material and Construction Analysis
Pin gauges are typically made from hardened tool steel or tungsten carbide to ensure durability and wear resistance, with precision ground cylindrical shapes for accurate measurement. Plug gauges also use similar high-quality materials, emphasizing robust construction with feature-specific designs to check hole dimensions and tolerances. Your choice between pin gauge and plug gauge depends on the application's precision requirements and the material hardness needed for reliable performance.
Typical Industrial Uses for Each Gauge
Pin gauges are typically used in precision measurement and inspection of small holes, slots, and grooves in manufacturing industries such as automotive and aerospace, ensuring tight tolerances in parts like fuel injectors and engine components. Plug gauges are commonly employed for verifying hole sizes, shapes, and depths in heavy machinery and metal fabrication, providing quick go/no-go checks for drilled or reamed holes in gear housings and structural components. Your choice between pin gauge and plug gauge depends on the specific application needs, such as measuring internal diameters or inspecting surface finish accuracy.
Advantages and Limitations of Pin Gauges
Pin gauges offer precise measurement of small hole diameters with high accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for quality control in manufacturing. Their simple design ensures durability and ease of use, but they are limited by fixed sizes and cannot measure variable or larger diameters. Your choice of pin gauge matters when consistent hole dimension verification is critical, though plug gauges may be preferred for go/no-go testing with different tolerance ranges.
Advantages and Limitations of Plug Gauges
Plug gauges offer precise internal diameter measurements with easy handling and quick inspection, ideal for verifying hole size in manufacturing processes. Their robustness ensures durability and consistent accuracy over repetitive use, reducing measurement errors and production delays. However, plug gauges are limited by their fixed size, requiring multiple gauges for different measurements and lacking the flexibility of adjustable instruments.
Choosing the Right Gauge for Your Application
Selecting the right gauge for your application hinges on the specific measurement needs: pin gauges excel at verifying hole diameters with high precision, while plug gauges are ideal for assessing both hole size and form, including tolerance limits. Pin gauges provide accurate reference standards for hole diameters in inspection processes, whereas plug gauges offer a go/no-go functionality critical for quality control in manufacturing. Understanding the dimensional requirements and tolerance specifications of your workpiece ensures choosing between pin gauges and plug gauges optimizes accuracy and efficiency in quality assurance.
Pin gauge vs plug gauge Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com