Spot welders create individual weld points by pressing metal surfaces together and applying electrical current, ideal for joining sheet metals at specific spots. Seam welders, on the other hand, produce continuous welds along a seam, offering airtight and watertight joints perfect for cylindrical or sheet metal assemblies.
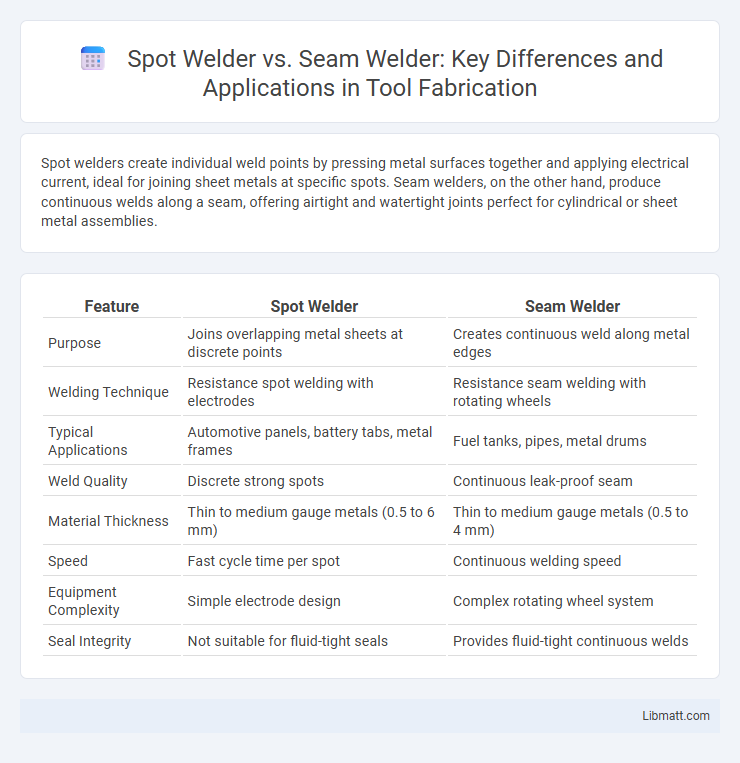
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spot Welder | Seam Welder |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Joins overlapping metal sheets at discrete points | Creates continuous weld along metal edges |
| Welding Technique | Resistance spot welding with electrodes | Resistance seam welding with rotating wheels |
| Typical Applications | Automotive panels, battery tabs, metal frames | Fuel tanks, pipes, metal drums |
| Weld Quality | Discrete strong spots | Continuous leak-proof seam |
| Material Thickness | Thin to medium gauge metals (0.5 to 6 mm) | Thin to medium gauge metals (0.5 to 4 mm) |
| Speed | Fast cycle time per spot | Continuous welding speed |
| Equipment Complexity | Simple electrode design | Complex rotating wheel system |
| Seal Integrity | Not suitable for fluid-tight seals | Provides fluid-tight continuous welds |
Introduction to Spot and Seam Welding
Spot welding joins metal sheets by applying pressure and heat through two copper electrodes to create discrete weld spots, ideal for sheet metal fabrication and automotive assembly. Seam welding generates continuous, leak-proof joints by using rotating wheel electrodes that deliver overlapping spot welds, commonly utilized in manufacturing fuel tanks and pipes. Both techniques provide strong welds but differ in application, with spot welding emphasizing isolated points and seam welding producing continuous seams.
Key Differences Between Spot and Seam Welding
Spot welding uses electrical resistance to join overlapping metal sheets at discrete points, creating strong, localized welds ideal for thin materials. Seam welding, on the other hand, produces a continuous, leak-proof joint by applying pressure and current through rotating wheels, making it suitable for applications requiring airtight seals. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate welding method based on material thickness, joint type, and durability requirements.
How Spot Welding Works
Spot welding joins metal sheets by applying heat and pressure through two copper electrodes at specific points, creating localized fusion without melting the entire surface. This precise electrical resistance heating method enables strong, fast, and efficient bonding ideal for high-volume production. Your projects benefit from spot welding's ability to produce consistent welds with minimal distortion and excellent structural integrity.
How Seam Welding Works
Seam welding works by using rotating wheel-shaped electrodes that apply pressure and continuous electric current along the metal edges to form a series of overlapping welds, creating a strong, continuous bond. This method is ideal for producing leak-proof joints in sheet metal applications such as fuel tanks, HVAC ducts, and automotive components. Seam welders offer consistent weld quality and speed, making them efficient for high-volume production requiring airtight and watertight seams.
Applications of Spot Welding
Spot welding is widely used in the automotive industry for joining sheet metal components, making it ideal for manufacturing car bodies and frames. It is also commonly applied in the production of electrical appliances and metal furniture due to its efficiency in creating strong, localized welds. Your projects requiring rapid and durable joining of thin metal sheets will benefit significantly from spot welding's precise and automated process.
Applications of Seam Welding
Seam welding is widely used in industries requiring airtight or watertight joints, such as automotive fuel tanks, beverage cans, and metal roofing. This technique enables continuous, leak-proof welds along metal sheets, making it ideal for manufacturing pipelines and HVAC systems. Its ability to produce strong, long-lasting seams enhances durability and corrosion resistance in various industrial applications.
Advantages of Spot Welders
Spot welders offer precise and rapid joining of metal sheets, making them ideal for automotive and manufacturing industries where efficiency is critical. They provide strong, localized welds with minimal distortion, preserving the integrity of surrounding materials. Their ability to automate and handle high production volumes enhances cost-effectiveness and consistency in industrial applications.
Advantages of Seam Welders
Seam welders offer continuous, airtight welds ideal for applications requiring strong, leak-proof joints such as fuel tanks, HVAC ducts, and sheet metal fabrication. Their ability to create consistent, uniform welds reduces the risk of weak points compared to spot welders, enhancing durability and structural integrity. Your production efficiency improves as seam welders automate long, straight or curved welds, minimizing manual intervention and increasing overall quality.
Choosing Between Spot and Seam Welding
Choosing between spot welder and seam welder depends on your project's specific requirements for joint type and strength. Spot welding excels in joining metal sheets with localized heat, providing fast and strong welds for automotive or metal fabrication tasks. Seam welding creates continuous, leak-proof joints ideal for applications requiring airtight or watertight seals, such as HVAC ductwork or fuel tanks.
Conclusion: Spot Welder vs Seam Welder
Spot welders deliver precise, high-strength welds ideal for joining overlapping metal sheets in automotive and manufacturing applications. Seam welders provide continuous welds along a joint, offering superior leak resistance and durability for tubing and cylindrical components. Your choice between spot welder vs seam welder depends on the specific welding requirements, such as weld type, material thickness, and desired joint strength.
Spot welder vs seam welder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com