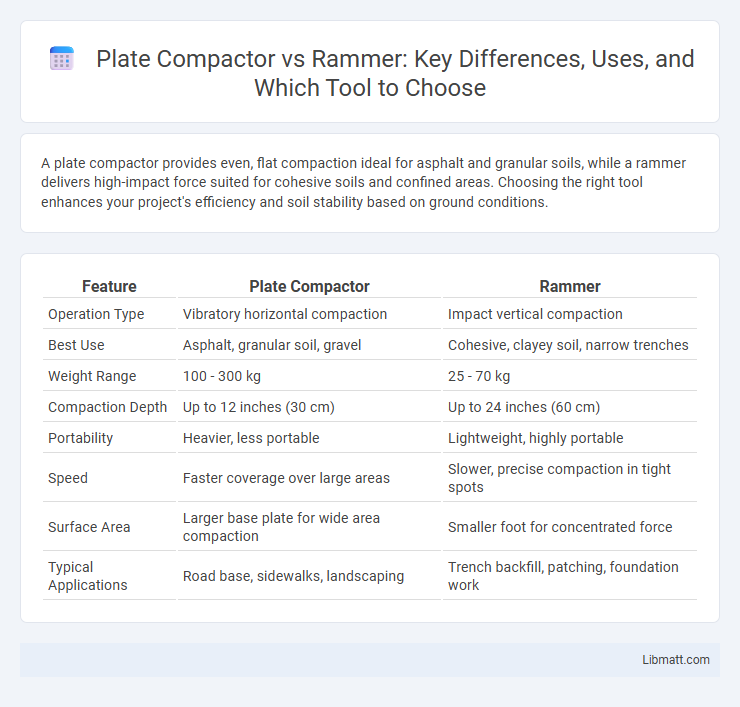
A plate compactor provides even, flat compaction ideal for asphalt and granular soils, while a rammer delivers high-impact force suited for cohesive soils and confined areas. Choosing the right tool enhances your project's efficiency and soil stability based on ground conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plate Compactor | Rammer |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Type | Vibratory horizontal compaction | Impact vertical compaction |
| Best Use | Asphalt, granular soil, gravel | Cohesive, clayey soil, narrow trenches |
| Weight Range | 100 - 300 kg | 25 - 70 kg |
| Compaction Depth | Up to 12 inches (30 cm) | Up to 24 inches (60 cm) |
| Portability | Heavier, less portable | Lightweight, highly portable |
| Speed | Faster coverage over large areas | Slower, precise compaction in tight spots |
| Surface Area | Larger base plate for wide area compaction | Smaller foot for concentrated force |
| Typical Applications | Road base, sidewalks, landscaping | Trench backfill, patching, foundation work |
Introduction to Plate Compactor and Rammer
Plate compactors and rammers serve distinct purposes in soil and asphalt compaction. A plate compactor uses a heavy, flat plate that vibrates to compact large, flat surfaces efficiently, ideal for granular soils and asphalt layers. Your choice depends on project needs, as rammers deliver high-impact force suited for cohesive soils and confined areas where deeper compaction is required.
Key Differences Between Plate Compactors and Rammers
Plate compactors deliver smooth, uniform compaction suitable for granular soils and asphalt with a vibrating base plate that spreads force evenly across a wide area. Rammers provide high-impact force with a narrower foot, ideal for cohesive soils and deeper, more aggressive soil compaction tasks. The choice between plate compactor and rammer depends on soil type, compaction depth, and project requirements for surface finish and compaction intensity.
Working Principles of Plate Compactors
Plate compactors operate using a heavy steel plate that vibrates vertically to compact soil, gravel, or asphalt surfaces by reducing air gaps and increasing density. The vibration is generated by an eccentric rotating weight powered by a gasoline or diesel engine, creating rapid, repetitive impacts that enhance soil stability. This mechanism is ideal for uniformly compressing granular materials in construction and landscaping projects.
Working Mechanism of Rammers
Rammers operate through a vertical, pounding action generated by a recoil or centrifugal mechanism, which delivers high-impact force to compact the soil. They use a piston driven by an internal combustion engine or hydraulic system, causing rapid up-and-down movements that penetrate deeper layers of soil for effective compaction in confined spaces. This mechanism makes rammers ideal for cohesive soils and trench works where precise, intensive compaction is required.
Applications: Where to Use Plate Compactors
Plate compactors are ideal for compacting granular soils, asphalt, and sand in construction projects like driveways, sidewalks, and small to medium-sized backfills. They provide uniform compaction on larger surface areas such as parking lots and trenches, making your site preparation more efficient. Unlike rammers, plate compactors are less effective on cohesive or clay soils, so select them based on the soil type and project scope.
Applications: Ideal Uses for Rammers
Rammers are ideal for compacting cohesive soils such as clay and silt in confined areas like trenches and around foundations where deep compaction is essential. Their high-impact force makes them suitable for installing utility trenches, backfilling foundations, and working in tight spaces that require vertical compaction. Unlike plate compactors, rammers provide superior compaction in restricted zones and irregular terrain, ensuring stability and preventing soil collapse.
Pros and Cons of Plate Compactors
Plate compactors offer excellent surface-level soil and asphalt compaction with a wide, flat base ideal for large, flat areas like driveways and pavements. They provide efficient, uniform compaction but may struggle on rocky or irregular terrain, where rammers are more effective. Plate compactors tend to be less maneuverable than rammers, which limits their use in tight spaces or trenches.
Pros and Cons of Rammers
Rammers offer superior soil penetration and compaction on cohesive and clay soils due to their high-impact force, making them ideal for trench work and narrow spaces. They are less effective on granular soils or large surface areas, where plate compactors excel. Rammers tend to be heavier and require more physical effort to operate, which can lead to increased operator fatigue on extended jobs.
Choosing the Right Compaction Equipment
Choosing the right compaction equipment depends on your project's soil type, depth requirements, and site constraints. Plate compactors are ideal for granular soils and surface compaction, offering efficiency on asphalt or concrete subbases, while rammers excel in cohesive soils like clay, providing deeper penetration and higher impact force. Understanding these distinctions ensures your project achieves optimal compaction, maximizing stability and durability.
Maintenance Tips for Plate Compactors and Rammers
Effective maintenance for plate compactors involves regularly checking and replacing the engine oil, cleaning the air filter, and inspecting the exciter system to ensure smooth operation. For rammers, maintaining the fuel system, tightening all bolts, and lubricating moving parts are critical to prevent breakdowns and extend equipment lifespan. Keeping your equipment well-maintained not only improves performance but also reduces downtime during important compaction projects.
Plate compactor vs rammer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com