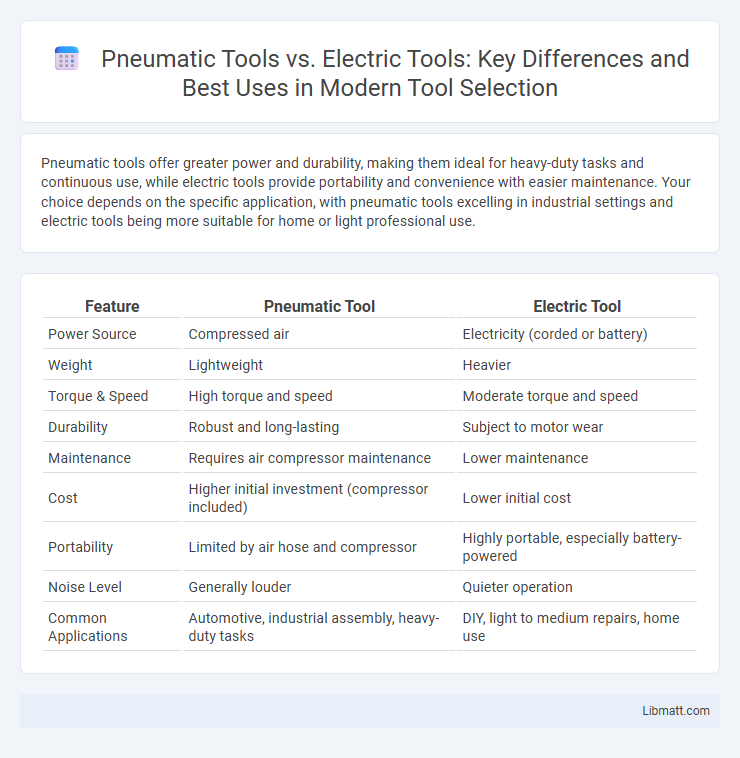
Pneumatic tools offer greater power and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks and continuous use, while electric tools provide portability and convenience with easier maintenance. Your choice depends on the specific application, with pneumatic tools excelling in industrial settings and electric tools being more suitable for home or light professional use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Tool | Electric Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Electricity (corded or battery) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Torque & Speed | High torque and speed | Moderate torque and speed |
| Durability | Robust and long-lasting | Subject to motor wear |
| Maintenance | Requires air compressor maintenance | Lower maintenance |
| Cost | Higher initial investment (compressor included) | Lower initial cost |
| Portability | Limited by air hose and compressor | Highly portable, especially battery-powered |
| Noise Level | Generally louder | Quieter operation |
| Common Applications | Automotive, industrial assembly, heavy-duty tasks | DIY, light to medium repairs, home use |
Introduction to Pneumatic and Electric Tools
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, offering high power-to-weight ratios and durability ideal for industrial and heavy-duty applications, whereas electric tools rely on electrical energy, providing convenience, portability, and versatility for both professional and DIY use. Understanding the fundamental differences between these tools helps you select the right equipment based on factors like efficiency, maintenance, and power requirements. Choosing between pneumatic and electric tools depends on your specific task demands and work environment.
Core Differences Between Pneumatic and Electric Tools
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, delivering high power-to-weight ratio and continuous operation without overheating, while electric tools rely on electricity, offering greater portability and ease of use with integrated motor controls. Pneumatic tools typically require an air compressor and are favored in industrial settings for heavy-duty tasks, whereas electric tools are more versatile for both professional and DIY applications due to their convenience and lower maintenance. Key differences include energy source, power delivery, maintenance needs, and suitability for prolonged or intermittent use.
Power Source and Performance Comparison
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, delivering consistent power ideal for heavy-duty tasks, while electric tools rely on batteries or direct electrical current, offering portability and ease of use. Pneumatic tools generally provide higher torque and longer run times without overheating, making them suitable for industrial applications, whereas electric tools excel in convenience and maintenance due to fewer moving parts. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize raw power and durability or flexibility and user-friendliness.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Pneumatic tools generally offer higher durability due to fewer moving parts and resistance to overheating, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial use. Maintenance for pneumatic tools primarily involves regular lubrication and air filter checks to prevent moisture and debris damage. Electric tools require careful electrical component upkeep and temperature monitoring, with batteries or cords needing replacement or repair more frequently compared to the simpler pneumatic systems.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
Pneumatic tools require careful handling of compressed air systems to prevent accidents, including regular inspection of hoses for leaks or damage and ensuring proper pressure settings to avoid sudden tool failures. Electric tools demand attention to electrical safety, such as checking cords for frays, using grounded outlets, and avoiding water exposure to minimize the risk of shocks or fires. Your choice between these tools should factor in the specific safety protocols and maintenance routines necessary to protect both the operator and the work environment.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Pneumatic tools generally have a lower upfront cost compared to electric tools but require an air compressor, which adds to the initial investment. Over time, electric tools tend to incur higher energy expenses, while pneumatic tools demand maintenance of both the compressor and the tool components, affecting long-term costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires considering initial purchase price, energy consumption, maintenance frequency, and tool longevity.
Portability and Accessibility Factors
Pneumatic tools require air compressors, limiting portability due to the need for a power source and added equipment bulk, while electric tools operate independently, offering greater mobility and ease of access in diverse locations. Your choice may depend on workspace setup, as pneumatic tools excel in fixed, industrial environments, whereas electric tools provide convenience for on-the-go tasks and remote job sites. Battery-powered electric tools enhance accessibility further by eliminating cords, making them ideal for both professional and DIY use.
Typical Applications in Various Industries
Pneumatic tools are widely used in automotive repair, construction, and manufacturing industries due to their high power-to-weight ratio and durability, ideal for tasks such as tightening bolts, cutting, and sanding. Electric tools dominate in woodworking, home improvement, and electronics assembly, offering precise control and portability for drilling, fastening, and intricate detailing. Both tool types serve critical roles, with pneumatic tools excelling in heavy-duty applications and electric tools preferred for versatility and ease of use in various industrial settings.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency
Pneumatic tools typically rely on compressed air generated by electric compressors, often resulting in higher overall energy consumption compared to electric tools that operate directly on electricity with greater efficiency. Electric tools generally produce lower carbon emissions during use because of their direct energy transfer and reduced waste heat generation, making them more environmentally friendly for continuous operation. To minimize Your environmental footprint, consider selecting electric tools with high energy efficiency ratings and sustainable power sources.
Choosing the Best Tool for Your Needs
Pneumatic tools offer superior power-to-weight ratios and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications, while electric tools provide greater portability and ease of use for general home or light commercial tasks. Consider the availability of a compressed air source, maintenance requirements, and long-term operating costs when selecting between pneumatic and electric tools. Prioritizing tool efficiency, job type, and user comfort ensures you choose the best tool that matches your specific work demands.
Pneumatic tool vs electric tool Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com