Ring gauges and plug gauges are precision tools used to measure the external and internal dimensions of parts, respectively. You can use a ring gauge to check the outside diameter of cylindrical objects, while a plug gauge verifies the inside diameter of holes to ensure parts meet exact specifications.
Table of Comparison
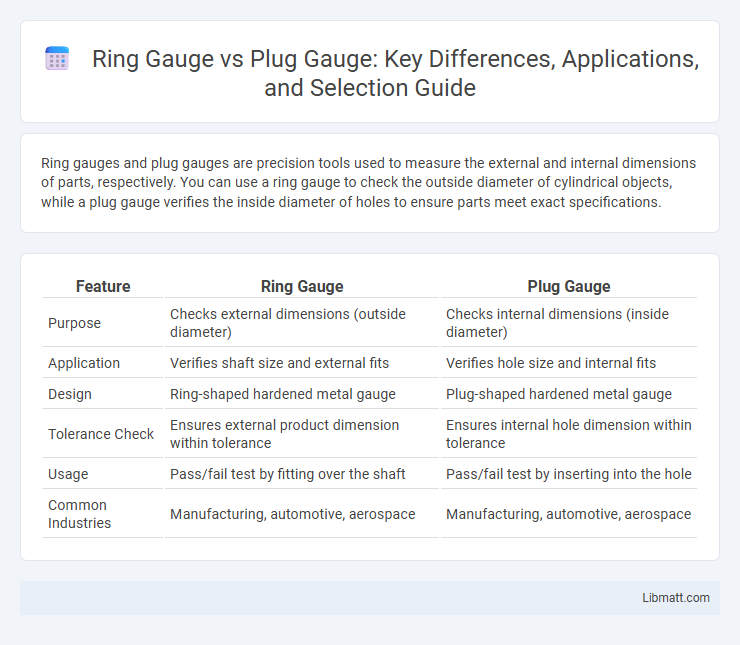
| Feature | Ring Gauge | Plug Gauge |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Checks external dimensions (outside diameter) | Checks internal dimensions (inside diameter) |
| Application | Verifies shaft size and external fits | Verifies hole size and internal fits |
| Design | Ring-shaped hardened metal gauge | Plug-shaped hardened metal gauge |
| Tolerance Check | Ensures external product dimension within tolerance | Ensures internal hole dimension within tolerance |
| Usage | Pass/fail test by fitting over the shaft | Pass/fail test by inserting into the hole |
| Common Industries | Manufacturing, automotive, aerospace | Manufacturing, automotive, aerospace |
Introduction to Ring Gauges and Plug Gauges
Ring gauges provide precise measurement of external dimensions by fitting over cylindrical parts, ensuring consistent diameter verification in manufacturing processes. Plug gauges measure internal dimensions by fitting into holes, verifying accuracy and tolerance of internal bores. Both tools are essential in quality control, offering reliable and repeatable dimensional checks for compliance with design specifications.
Definition and Function of Ring Gauges
Ring gauges serve as precise cylindrical tools used to verify external dimensions of cylindrical parts by ensuring they fit accurately within set tolerances. They function as master limits, typically representing the maximum acceptable outside diameter in go/no-go gauging systems. These gauges provide high accuracy in quality control processes by confirming whether manufactured parts meet specified dimensional standards.
Definition and Function of Plug Gauges
Plug gauges serve as precise inspection tools designed to verify the internal dimensions and tolerances of holes, ensuring accurate fit and functionality. They consist of a cylindrical metal piece that fits into the hole, allowing inspectors to check if the hole diameter meets specified limits, typically using go/no-go standards. Unlike ring gauges that measure external dimensions, plug gauges focus on internal measurements to maintain quality control in manufacturing processes.
Key Differences Between Ring Gauge and Plug Gauge
Ring gauges measure the external diameters of cylindrical objects, ensuring parts fit within specified tolerances, while plug gauges verify internal diameters, checking hole sizes for accuracy. The primary difference lies in their application: ring gauges assess outside dimensions, and plug gauges inspect inside dimensions. Your quality control process benefits from using both to maintain precision in manufacturing tolerances.
Applications of Ring Gauges in Industry
Ring gauges play a critical role in manufacturing industries by providing precise measurements for the external diameter of cylindrical parts, ensuring they meet strict tolerance requirements. Commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering sectors, ring gauges facilitate rapid inspection and quality control of shafts, pins, and other cylindrical components. Their application enhances production efficiency by enabling quick go/no-go checks that maintain consistency and prevent defective parts from advancing in the assembly process.
Applications of Plug Gauges in Industry
Plug gauges are essential tools for measuring internal dimensions such as hole diameters in manufacturing and quality control processes. Their applications span industries like automotive, aerospace, and machinery production where precise hole tolerances ensure proper fit and function. Using plug gauges helps maintain stringent quality standards, preventing defects and ensuring your products meet exact specifications.
Advantages of Using Ring Gauges
Ring gauges offer precise external diameter measurements, ensuring consistent quality control for cylindrical parts and enhancing manufacturing accuracy. They provide durability and long-term reliability due to their solid construction and resistance to wear, reducing the need for frequent recalibration. Using ring gauges streamlines inspection processes by enabling rapid go/no-go assessments, improving production efficiency and minimizing measurement errors.
Advantages of Using Plug Gauges
Plug gauges offer precise measurement of internal dimensions, ensuring accurate assessment of hole diameters and depths. Their solid construction provides consistent calibration, reducing measurement errors in quality control processes. Using plug gauges in your inspection routine enhances reliability and speeds up verification of manufacturing tolerances.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Ring Gauge and Plug Gauge
When selecting between ring gauge and plug gauge, factors such as measurement type, tolerance requirements, and application precision play a crucial role. Ring gauges are ideal for inspecting external diameters of cylindrical parts with high accuracy, while plug gauges measure internal diameters and are used to verify hole sizes. Material hardness, gauge calibration standards, and ease of use in production environments also influence the choice for optimal quality control.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Gauge for Your Needs
Choosing between a ring gauge and a plug gauge depends on the specific measurement requirements and the part's geometry. Ring gauges excel in verifying external dimensions like shaft diameters with high precision, while plug gauges are ideal for inspecting internal dimensions such as hole diameters and bores. Selecting the right gauge ensures accurate quality control and minimizes measurement errors in manufacturing processes.
Ring gauge vs plug gauge Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com